(Created page with "<html> <div class="oneColumn alert_box"> <center>This page is under active development and is in draft form.</center> </div> <br><br><br><br><br> <div class="oneColumn"> <!-...") |
m (Protected "Tracks/Food Nutrition" ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Mobile}} | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <div class="clear"></div> | |
| − | + | <div class="oneColumn"> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
Until 2014, Food and Energy were included as a track in iGEM. In 2015, we separated these two concepts into the Food and Nutrition Track and the Energy Track. We want to highlight that while there is a lot of crossover in these two track ideas, they seek to resolve fundamentally different problems. | Until 2014, Food and Energy were included as a track in iGEM. In 2015, we separated these two concepts into the Food and Nutrition Track and the Energy Track. We want to highlight that while there is a lot of crossover in these two track ideas, they seek to resolve fundamentally different problems. | ||
| Line 94: | Line 88: | ||
| − | < | + | </div> |
| − | + | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
{{2016Bottom}} | {{2016Bottom}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:05, 10 June 2016
Until 2014, Food and Energy were included as a track in iGEM. In 2015, we separated these two concepts into the Food and Nutrition Track and the Energy Track. We want to highlight that while there is a lot of crossover in these two track ideas, they seek to resolve fundamentally different problems.
Everybody needs to eat. But with over 7 billion people on the planet, the problem of producing enough food and energy is complex and multi-faceted. While nations have different ideas about cuisine, everybody needs roughly the same number of calories per day. These calories can come from many sources, but world agricultural land and water use is increasingly stretched to cope with our current population. Better solutions that don't rely on unsustainable fishing practices, increased arable land and industrial agriculture are needed to cope with our ever-expanding population.
You will find images and abstracts of the winning Food or Energy teams from 2011 to 2013 in the page below. Also, follow the links below to see projects from all the Food or Energy track teams.
- iGEM 2015 Food and Nutrition team list
- iGEM 2014 Food and Nutrition team list
- iGEM 2013 Food and Nutrition team list
Recent Food and Energy projects to win best in track
Winning Food and Energy projects in 2013 Undergrad: The FerriTALE
Calgary
Project abstract: Outbreaks of foodborne illnesses are a growing problem for food safety and public health. Whether in your water, salad or steak, pathogenic E. coli causes upwards of 250,000 illnesses every year. To solve this problem, iGEM Calgary is developing the FerriTALE to detect harmful E. coli. It uses engineered proteins that detect and report the presence of dangerous E. coli in a sample. The detector, TALE, binds to genomic markers specific to dangerous E. coli. Next, our TALEs are attached to the scaffold and reporter, Ferritin, that rapidly alerts the user to the presence of E. coli through a visible color change. We have integrated these proteins into a handheld device, similar to a home pregnancy test, that tells the user if dangerous E. coli is present. Moving forward, the FerriTALE can be tailored to detect other pathogens as the basis of a powerful new detection platform.
Winning Food and Energy projects in 2012: Food Warden
Groningen
The Groningen 2012 iGEM team also won the Grand Prize BioBrick trophy at the World Championship Jamboree.
Project abstract :Every year, one third of global food production -1.3 billion tons of food- is thrown away, partially due to the “best before” dating system. iGEM Groningen 2012 seeks to provide an alternative method of assessing edibility: the Food Warden. It uses an engineered strain of Bacillus subtilis to detect and report volatiles in spoiling meat. The introduced genetic construct uses a promoter to trigger a pigment coding gene. This promoter, identified by microarray analysis, is significantly upregulated in the presence of volatiles from spoiling meat. The activity of the promoter regulates the expression of the pigment reporter and will be visible to the naked eye. For safe usage of the system, spores of our engineered strain are placed into one half of a semi-permeable capsule, the second containing a calibrated amount of nutrients. Breaking the barrier between the two compartments allows germination and growth, thereby activating the spoiling-meat sensor.
Winning Food and Energy project 2011: (Tie) Washington and Yale
Washington
The University of Washington 2011 iGEM team also won the Grand Prize BioBrick trophy at the World Championship Jamboree.
Project abstract: Synthetic biology holds great promise regarding the production of important compounds, and the degradation of harmful ones. This summer, we harnessed the power of synthetic biology to meet the world's needs for fuel and medicine. Make It: We constructed a strain of Escherichia coli that produces a variety of alkanes, the main constituents of diesel fuel, by introducing a pair of genes recently shown convert fatty acid synthesis intermediates into alkanes. Break It: We identified a protease with gluten-degradation potential, and then reengineered it to have greatly increased gluten-degrading activity, allowing for the breakdown of gluten in the digestive track when taken in pill form. Finally, to enable next-generation cloning of standard biological parts, BioBrick vectors optimized for Gibson assembly were constructed and used to construct the Magnetosome Toolkit: genes for biofabrication of magnetic particles.
Yale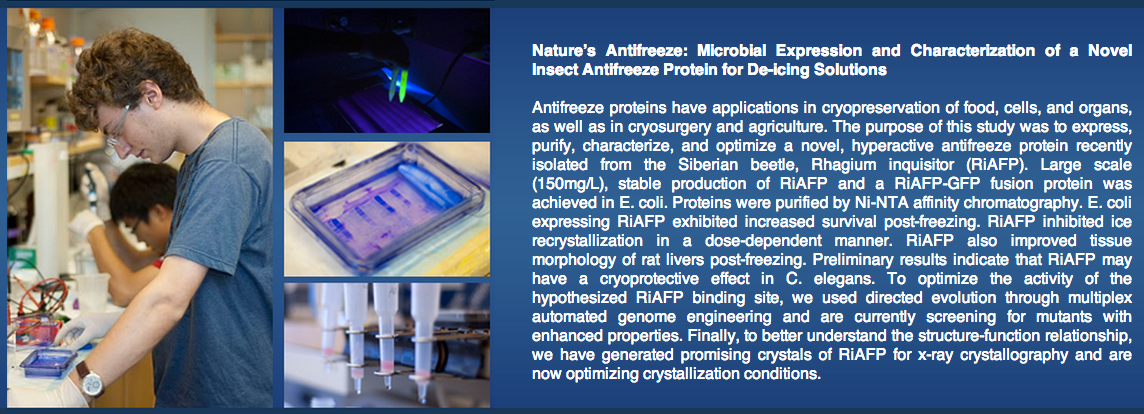
Project abstract: Antifreeze proteins have applications in cryopreservation of food, cells, and organs, as well as in cryosurgery and agriculture. The purpose of this study was to express, purify, and characterize a novel, hyperactive antifreeze protein recently isolated from the Siberian beetle, Rhagium inquisitor (RiAFP). Large scale (150mg/L), stable production of RiAFP and a RiAFP-GFP fusion protein was achieved in E. coli. Proteins were purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. E. coli expressing RiAFP exhibited increased survival post-freezing. RiAFP inhibited ice recrystallization in both splat and capillary assay. To optimize the activity of the hypothesized RiAFP ice binding site, we are using directed evolution through multiplex automated genome engineering (MAGE). Finally, we are further optimizinge our crystallization conditions for RiAFP to better understand the structure-function relationship, as well as conducting post-freezing survival assays in C. elegans.

