| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
We expressed and characterized it in mammalian cells, where it served as the sensor that translates the ultrasound stimulation | We expressed and characterized it in mammalian cells, where it served as the sensor that translates the ultrasound stimulation | ||
into calcium ion influx, thereby playing a central role our design of ultrasound responsive cells as well as cells responsive to the touch (Touchpaint).</p> | into calcium ion influx, thereby playing a central role our design of ultrasound responsive cells as well as cells responsive to the touch (Touchpaint).</p> | ||
| − | + | <div> | |
| + | <figure data-ref="2"> | ||
| + | <img class="ui medium image" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/e/ec/T--Slovenia--BBa_K1965000.PNG"> | ||
| + | <figcaption><b>Localization and expression of mechanosensitive ion channel MscS. </b><br/>HEK293 cells were transfected with MscS. Expression by Western blot and localization by confocal microscopy were analyzed using anti-HA antibodies. | ||
| + | (A) Scheme of bacterial ion channel MscS | ||
| + | (B) Ion channel MscS is localized on plasma membrane. HEK293 cells were transfected with the MscS:HA plasmid. 24 h after transfection cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized and stained with anti-HA antibodies. Localization was confirmed with confocal microscopy. | ||
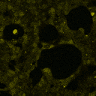
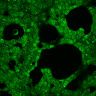
| + | (D) Ion channels expressed in HEK293 cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids, encoding gas vesicle-forming proteins GvpA and GvpC. 48 h after transfection cells were collected, lysed and total protein concentration was measured. 50ng of proteins were loaded on SDS page gels. After separation by size, proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane by western blot. Membranes were then immunoblotted with anti-FLAG or anti-AU1 antibodies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
<div style="clear:both; width:70%; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;"> | <div style="clear:both; width:70%; margin-left:auto; margin-right:auto;"> | ||
Revision as of 14:26, 18 October 2016
New Basic part
The BioBrick nominated for best part is MscS (BBa_K1965000) from our Mechanosensing Collection. This part
contains the coding sequence of the bacterial mechanosensitive channel of small conductance (MscS). It has been previously described as an important receptor involved
in bacterial sensing of mechanical stress.
We expressed and characterized it in mammalian cells, where it served as the sensor that translates the ultrasound stimulation
into calcium ion influx, thereby playing a central role our design of ultrasound responsive cells as well as cells responsive to the touch (Touchpaint).

HEK293 cells were transfected with MscS. Expression by Western blot and localization by confocal microscopy were analyzed using anti-HA antibodies. (A) Scheme of bacterial ion channel MscS (B) Ion channel MscS is localized on plasma membrane. HEK293 cells were transfected with the MscS:HA plasmid. 24 h after transfection cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized and stained with anti-HA antibodies. Localization was confirmed with confocal microscopy. (D) Ion channels expressed in HEK293 cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids, encoding gas vesicle-forming proteins GvpA and GvpC. 48 h after transfection cells were collected, lysed and total protein concentration was measured. 50ng of proteins were loaded on SDS page gels. After separation by size, proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane by western blot. Membranes were then immunoblotted with anti-FLAG or anti-AU1 antibodies.


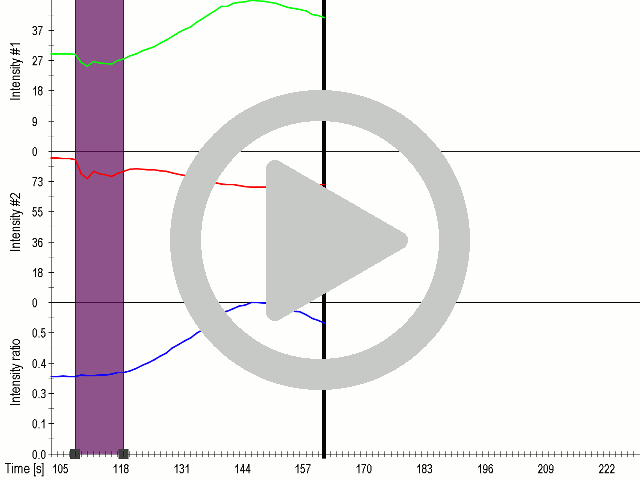
(A) Schematic representation of a stimulation sequence and (B) signal parameters used for stimulation. (C) and (D)Cells expressing MscS showed increased sensitivity to ultrasound stimulation in comparison to the cells without exogenous mechanosensitive channel. HEK293 cells expressing MscS channels or control cells transfected with vector were stimulated with ultrasound for 10 s and calcium influx was recorded in real time (D) using a confocal microscope. For comparison cells without ectopic MscS were used. Fluo-4 (D, green line) and Fura Red dyes (D, red line) were used for ratiometric calcium imaging. (D) Ratio (blue line) was calculated from fluorescence intensities of Fura Red and Fluo-4 using CaPTURE.



