Contents
Overview
As part of our project, we aimed to turn Streptococcus thermophilus into a chassis organism that could potentially be used by future iGEM teams in food and nutrition projects. Part of this undertaking was the identification and characterization of S. thermophilus promoters for use in S. thermophilus constructs. We used fluorescence to quantify the strength of three S. thermophilus promoters and compared them to six different Anderson family promoters with known relative strengths, in E. coli.
The Promoters
We tested and characterized the strengths of three previously identified lactic acid bacterial promoters:
- pHLBA: A constitutive promoter responsible for the expression of histone-like proteins in Lactobcillus bulgaricus and other lactic acid bacteria.[1]
- p32: A constituve promoter used in expression vectors in S. thermophilus.[2]
- p25: A constituve promoter identified in a genome survey for S. thermophilus promoters.[2]
The following Anderson family promoters were used as a known comparison, relative strength in parentheses: J23100 (100%), J23101 (70%), J23106 (47%), J23105 (24%), J23117 (6%), J23113 (1%)
Protocol
Assembly
We created two reporter constructs for each promoter:
- Medium RBS GFP: Promoter + E5501 (B0032 + E0040)
- Strong RBS GFP: Promoter + I13500 (B0034 + E0040)
The three S. thermophilus promoters were synthesized as oligos by IDT and ligated into E5501 and I13500 cut with EcoRI and XbaI. E5501 and I13500 were cut with XbaI and PstI and ligated into existing Anderson promoter plasmids cut with SpeI and PstI. This resulted in a total of 18 constructs.
Transformation and Culturing
E5501, I13500 and all 18 constructs were transformed into E. coli TOP10 cells made competent with calcium chloride according to a standard transformation protocol. Transformants were plated out on chloramphenicol agar and cultured overnight at 37⁰C. Three colonies from each plate were subsequently restreaked to rule out false positives and provide a fresh supply of colonies for the measurement step. Three colonies from each restreak plate were picked and inoculated in 3ml of L-broth and chloramphenicol overnight at 37⁰C and 225rpm in a shaking incubator. Three non-transformed TOP10 colonies were also picked and cultured to serve as non-fluorescent controls alongside the promoter-less E5501 and I13500 controls. Therefore, each construct was being measured using three biological replicates. E5501 and I13500 constructs were cultured and measured on separate days to reduce the volume of samples
Measurement
Following removal from the incubator, 100µl from each overnight was added to a single well in a 96-well plate. Sampling was repeated three times for each biological replicate, yielding a total of 9 samples for each promoter-reporter construct. Each promoter’s samples occupied 9 wells in a single row. Fluorescence and OD600 measurements were performed using a Bio-Tek Synergy HT plate reader using GFP excitation and emission spectra with a gain of 40 and a read height of 10mm Following measurement, data was exported to excel and standardized for an OD600 of 1.
Results
Measurements using the strong RBS variants revealed the expected order of promoter strength for Anderson promoters and showed that the S. thermophilus promoters were relatively strong:
Figure 1: Mean fluorescence values for I13500 under the control of various promoters. Red represents S. thermophilus promoters, blue represents Anderson family promoters. Error bars represent standard deviation for each set of samples.
pHLBA was the strongest S. thermophilus promoter, exhibiting 93% the fluorescence value of J23100, followed by p32 which exhibited 81% J23100 fluorescence. P25 was the weakest promoter at 30.8% the fluorescence value of J23100. However, it was still moderately strong.
While the order of Anderson promoter strengths fits in with prior measurements, the precise values were different than those previously reported:
- J23101 exhibited fluorescence 70% as strong as J23100, consistent with prior measurements.
- J23106 exhibited fluorescence 24% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 47%.
- J23105 exhibited fluorescence 14% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 24%.
- J23117 exhibited fluorescence 1% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 6%.
- J23113 exhibited fluorescence 0.4% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 1%. J23113 fluorescence was lower than that of the I13500 promoter-less control and indistinguishable from the TOP10 untransformed control.
Fluorescence measurements for constructs using E5501 (GFP with B0032, a medium promoter) showed slightly different results:
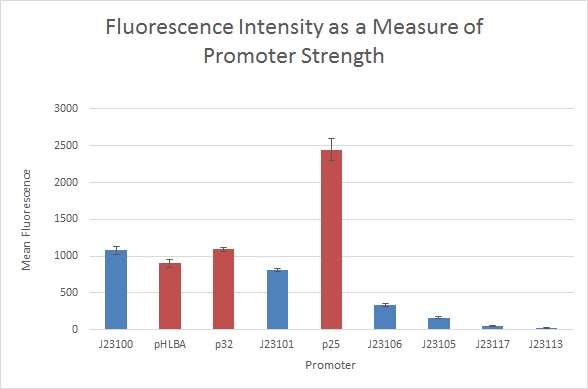 Figure 2: Mean fluorescence values for E5501 under the control of various promoters. Red represents S. thermophilus promoters, blue represents Anderson family promoters. Error bars represent standard deviation for each set of samples. Promoters are ordered according to their strength in Figure 1.
Figure 2: Mean fluorescence values for E5501 under the control of various promoters. Red represents S. thermophilus promoters, blue represents Anderson family promoters. Error bars represent standard deviation for each set of samples. Promoters are ordered according to their strength in Figure 1.
P25 showed a much higher strength than expected: 227% that of J23100.
p32+E5501 fluorescence was not significantly different from that of J23100 (failed p=0.05 T test) in contrast to p32+I13500. pHLBA+E5501 exhibited 83% the fluorescence of J23100+E5501, in contrast to 93% in I13500.
The Anderson promoters also showed slightly different strengths relative to each other than in the I13500 experiment:
- J23101 exhibited fluorescence 75% as strong as J23100, consistent with prior measurements.
- J23106 exhibited fluorescence 31% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 47% and 24% in I13500.
- J23105 exhibited fluorescence 15% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 24%, and 14% in I13500.
- J23117 exhibited fluorescence 5% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 6% and 1% in I13500.
- J23113 exhibited fluorescence 2% as strong as J23100, compared to the reported 1% and 0.4% in I13500. However, J23113 fluorescence was still indistinguishable from the TOP10 untransformed control.
Alternative Results
A graph was constructed with the data collected showing the fluorescence of GFP under expression of the various promoters and ribosome binding sites B0034 (on the right) and B0032 (on the left). A plate reader was used which measured the OD of every sample simultaneously to the fluorescence measurements, so OD was normalised across all samples in order to get comparable fluorescence readings.
Figure 2: Graph of strength of fluorescence expressed by E. coli cells under 8 different promoters. Measurements with strong RBS B0034 are in light green, and measurements with weak RBS are in a darker green. Error bars represent standard deviation for each set of samples.
Figure 2 shows that the S. thermophiluspromoters were relatively strong, yielding 93% (pHLBA), 81% (p32) and 30% (p25) of the fluorescence values of J23100, the strongest modified Anderson promoter. Fluorescence levels in the constructs using weak RBS B0032 were significantly reduced, but relative promoter strengths were equivalent. The unusually high level of fluorescence for promoter p25 with B0032 can be attributed to the fact that the plasmid had dimerised. The dimerisation was verified with a gel electrophoresis but due to time constraints we were unable to carry out a second set of fluorescence measurements in order to obtain a correct value for fluorescence of GFP under p25.
Discussion
Several discrepancies between the two experiment were apparent. Although we did not have the time to repeat the experiments, we attempted to explain them using the available data.
p25
When under the control of p25, E5501 exhibited fluorescence comparable to I13500 (~2300 arbitrary units). This value was much higher than for E5501 under the control of all other promoters. We first believed that there had been a mistake during assembly and I13500 had been used instead. However, sequencing revealed that the p25+E5501 plasmid had dimerized in all three biological replicates. While this may the cause of the unexpected fluorescence readings, we did not have the time to repeat testing.
J23100 Fluorescence in E5501
Both p32 and pHLBA exhibited higher promoter strength relative to J23100 in E5501 compared to I13500. The other Anderson promoters showed the same increase in strength relative to J23100. However, this may mean there were problems with J23100+E5501 expression.
J23113+E5501 stronger than expected (2% instead of 1% or 0.04% in the I13500 experiment) but also no different than the untransformed control, it is likely that J23100+E5501 itself was not being expressed as strongly as possible. This may account for the apparently equal fluorescence between J23100 and p32. Unfortunately, time constraints prevented us from repeating the experiment to see if the result was down to experimental error.
References
- ↑ Chouayekh, H., Serror, P., Boudebbouze, S. and Maguin, E. (2009). Highly efficient production of the staphylococcal nuclease reporter in Lactobacillus bulgaricus governed by the promoter of the hlbA gene. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 293(2), pp.232-239.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Slos, P., Bourquin, J., Lemoine, Y. and Mercenier, A. (1990). Isolation and Characterization of Chromosomal Promoters of Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus. APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, 57(5), pp.1333-1339.




