Zigapusnik (Talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| (119 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<script type="text/javascript" | <script type="text/javascript" | ||
src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/semantic-min-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/semantic-min-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | ||
| − | <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/custom-css?action=raw&ctype=text/css"> | + | <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" |
| − | <script type="text/javascript" src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/custom-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/custom-css?action=raw&ctype=text/css"> |
| + | <script type="text/javascript" | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/custom-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | ||
<script type="text/javascript" | <script type="text/javascript" | ||
src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/zitator-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | src="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/zitator-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | ||
<script type="text/javascript" | <script type="text/javascript" | ||
src="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/bibtexparse-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | src="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/libraries/bibtexparse-js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript"></script> | ||
| − | + | <style> | |
| − | < | + | .container { |
| − | + | position: relative; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | .module1 { | |
| − | + | position: absolute; | |
| − | + | top: 220px; | |
| − | + | left: 10px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | .module2 { | |
| − | + | position: absolute; | |
| − | + | bottom: 90px; | |
| − | + | left: 220px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | .module3 { | |
| − | + | position: absolute; | |
| − | + | top: 180px; | |
| − | + | right: 350px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | .module4 { | |
| − | + | position: absolute; | |
| − | + | bottom: 15px; | |
| − | + | right: 380px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | .igemSign { | |
| − | border-radius: 15px; | + | position:absolute; |
| − | + | bottom: 80%; | |
| − | + | left: 100%; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | /* Popup container - can be anything you want */ | |
| − | + | .popup { | |
| − | + | display: inline-block; | |
| − | + | cursor: pointer; | |
| − | + | -webkit-user-select: none; | |
| − | + | -moz-user-select: none; | |
| − | + | -ms-user-select: none; | |
| − | + | user-select: none; | |
| − | + | padding: 10px 10px; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | /* The actual popup */ | |
| − | + | .popup .popuptext { | |
| − | + | padding: 10px 10px; | |
| + | visibility: hidden; | ||
| + | width: 350px; | ||
| + | background-color: #555; | ||
| + | color: #fff; | ||
| + | text-align: center; | ||
| + | border-radius: 6px; | ||
| + | position: absolute; | ||
| + | z-index: 100; | ||
| + | font-size: 12px; | ||
| + | line-height: 18px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Toggle this class - hide and show the popup */ | ||
| + | .popup .show { | ||
| + | visibility: visible; | ||
| + | -webkit-animation: fadeIn 1s; | ||
| + | animation: fadeIn 1s; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | /* Add animation (fade in the popup) */ | ||
| + | @-webkit-keyframes fadeIn { | ||
| + | from { | ||
| + | opacity: 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | to { | ||
| + | opacity: 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @keyframes fadeIn { | ||
| + | from { | ||
| + | opacity: 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | to { | ||
| + | opacity: 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .container img { | ||
| + | display: block; | ||
| + | margin-left: auto; | ||
| + | margin-right: auto; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | .corners { | ||
| + | border-radius: 15px; | ||
| + | border: 2px solid #000000; | ||
| + | padding: 15px; | ||
| + | margin-left: 15px; | ||
| + | margin-bottom: 15px; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | </style> | ||
| + | </head> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | <script> | ||
| + | $(document).ready( | ||
| + | function () { | ||
| + | /*var getImgs = function () { | ||
| + | var imgs = []; | ||
| + | $('img').each(function () { | ||
| + | console.log("image detected"); | ||
| + | var data = $(this).data('alt'); | ||
| + | imgs.push(data); | ||
| + | }); | ||
| + | return imgs; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | var imgs = getImgs(); | ||
| + | //preload images | ||
| + | var image = []; | ||
| + | $.each(imgs, function (index) { | ||
| + | console.log("loading resource"); | ||
| + | image[index] = new Image(); | ||
| + | image[index].src = imgs[index]; | ||
| + | });*/ | ||
| + | var images = new Array(); | ||
| + | function preload() { | ||
| + | for (i = 0; i < preload.arguments.length; i++) { | ||
| + | images[i] = new Image(); | ||
| + | images[i].src = preload.arguments[i]; | ||
| + | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | preload( | |
| − | + | "//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png", | |
| − | + | "//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/9/92/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme1.png", | |
| − | + | "//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f6/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme2.png", | |
| − | + | "//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/5/54/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme3.png", | |
| − | + | "//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/1/12/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme4.png" | |
| − | + | ); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ); | |
| − | + | function loadImage(sourceImage, popupname) { | |
| − | + | console.log(sourceImage); | |
| − | + | var image = document.getElementById("projectScheme"); | |
| − | + | image.src = sourceImage; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | //var rect = image.getBoundingClientRect(); | |
| − | + | //console.log(rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom, rect.left); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | var popup = document.getElementById(popupname); | |
| − | + | //popup.style.top = ((rect.bottom - rect.top)/2).toString().concat("px"); | |
| − | + | //popup.style.left = ((rect.right - rect.left)/2).toString().concat("px"); | |
| − | + | //console.log((rect.right - rect.left)/2, (rect.bottom - rect.top)/2); | |
| − | + | popup.classList.toggle('show'); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | function tooglePopup() { | |
| − | + | var popup = document.getElementById("igemSign"); | |
| − | + | popup.classList.toggle('show'); | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | </script> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <div id="example"> | |
| − | + | <div class="pusher"> | |
| − | + | <div class="full height"> | |
| − | + | <div class="banana"> | |
| − | + | <a href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia"> | |
| − | + | <img class="ui medium sticky image" src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/d1/T--Slovenia--logo.png"> | |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <div class="ui vertical sticky text menu"> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia" style="color:#DB2828;"> | |
| − | + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> | |
| − | + | <b>Home</b> | |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="#intro" style="margin-left: 10%"> | |
| − | + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> | |
| − | + | <b>Project</b> | |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="#experts" style="margin-left: 10%"> | |
| − | + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> | |
| − | + | <b>Abstract for experts</b> | |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="#plain" style="margin-left: 10%"> | |
| − | <br /> | + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> |
| − | + | <b>Abstract in plain English</b> | |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="#achievements" style="margin-left: 10%"> | |
| − | + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> | |
| − | Cells were transfected with constructs coding for the bacterial ion channel MscS, gas vesicles (GvpA and GvpC) and a Ca-dependent | + | <b>Achievements</b> |
| − | + | </a> | |
| − | + | <a class="item" href="#requirements" style="margin-left: 10%"> | |
| + | <i class="selected radio icon"></i> | ||
| + | <b>Medal requirements</b> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | <a class="item" href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Idea/Challenge"> | ||
| + | <i class="chevron circle right icon"></i> | ||
| + | <b>Idea</b> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | <span> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | </span> | ||
| + | <div style = "position:fixed; width:14%; left:3%; bottom:3%;"> | ||
| + | <a href = "//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Proof"><img onmouseenter="tooglePopup();" onmouseleave="tooglePopup();" class="ui large circular image" src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/6/67/T--Slovenia--iGEM-gif.gif"></a> | ||
| + | <div class="popup igemSign"> | ||
| + | <span class="popuptext" id="igemSign">Touchpaint - detecting touch by light. The iGEM symbol was drawn with a glass rod letter by letter on engineered human cells and imaged by a camera. | ||
| + | Cells were transfected with constructs coding for the bacterial ion channel MscS, gas vesicles (GvpA and GvpC) to enhance mechanosensing and a Ca-dependent | ||
| + | cyclic split luciferase reporter to visualize the signal by light.</span> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="article" id="context"> | |
| − | + | <!-- menu goes here --> | |
| − | + | <!-- content goes here --> | |
| − | + | <div class="main ui citing justified container"> | |
| − | + | <div> | |
| − | + | <h1 class="ui centered dividing header" style="font-size: 3rem"><span id="intro" class="section colorize"> </span>Sonicell | |
| − | + | </h1> | |
| − | + | <div class="ui segment"> | |
| − | + | <p>For the therapy of diseases such as diabetes, we require a system of drug delivery that is fast, controllable and noninvasive. Engineering cells to produce drugs in the tissue is a promising direction. However, in most genetic circuits designed by synthetic biology the response is delayed due to the need to transcripe and translate the mediators. Project Sonicell introduces exciting foundational advances to synthetic biology aimed to | |
| − | + | enable rapid cellular response to a combination of external stimuli such as sound, light | |
| − | + | or chemical compounds. This system is composed of a module for <b>enhanced sensitivity of | |
| − | + | cells to ultrasound or other mechanical stimuli</b>, sensed by a calcium-dependent reporter, | |
| − | + | and a module for integration of a combination of several input signals into a <b>signaling | |
| − | + | pathway based on proteolysis </b> by a collection of orthogonal proteases. Finally, the proteases were | |
| − | + | designed to cleave an endoplasmic reticulum retention signal from target proteins, which | |
| − | + | results in <b>secretion of premade proteins</b>.</p> | |
| − | + | <div> | |
| − | + | <div class="container"> | |
| − | + | <img width="100%" onresize="relativeCoords();" onload="relativeCoords();" | |
| − | + | style="border-radius: 15px;" | |
| − | + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png" | |
| − | + | alt="project scheme" usemap="#projectmap" id="projectScheme"/> | |
| − | + | <map name="projectmap"> | |
| − | + | <area id="area1" class="popup" shape="poly" coords="" alt="module1" | |
| − | + | onmouseover="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/9/92/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme1.png', 'module1')" | |
| − | + | onmouseout="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png', 'module1')" | |
| − | + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Mechanosensing/Overview"> | |
| − | + | <area id="area2" class="popup" shape="poly" coords="" alt="module1" | |
| − | + | onmouseover="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/5/54/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme3.png', 'module2')" | |
| − | + | onmouseout="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png', 'module2')" | |
| − | + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Protease_signaling/Logic"> | |
| − | + | <area id="area3" class="popup" shape="poly" coords="" alt="module1" | |
| − | + | onmouseover="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f6/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme2.png', 'module3')" | |
| − | + | onmouseout="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png', 'module3')" | |
| − | + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Protease_signaling/Overview"> | |
| − | + | <area id="area4" class="popup" shape="poly" coords="" alt="module1" | |
| − | + | onmouseover="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/1/12/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme4.png', 'module4')" | |
| − | + | onmouseout="loadImage('//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/c/c2/T--Slovenia--Main-scheme0.png', 'module4')" | |
| − | + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Implementation/ProteaseInducible_secretion"> | |
| − | + | </map> | |
| − | + | <div class="popup module1"> | |
| − | + | <span class="popuptext" id="module1"><b>Enhanced mechanosensing:</b><br> | |
| − | + | Sensitivity of mammalian cells to ultrasound or other mechanical stimuli was enhanced by the introduction | |
| − | + | of mechanosensitive ion channels and/or by the expression of protein gas vesicles from bacteria. Influx of | |
| − | + | calcium through channels is sensed by formation of a complex between calmodulin and M13 peptide that can | |
| − | + | result in a rapid light emission by cells (used for cell painting) or reconstitution of a split protease.</span> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="popup module2"> | |
| − | + | <span class="popuptext" id="module2"><b>Protease based signaling <br/>and information processing:</b><br/> | |
| − | + | Combinations of proteolytic activities against specific targets resulted in activation of a reporter or another | |
| − | + | protease, which forms the basis for the design of a new type of rapid signaling pathways and construction of | |
| − | + | logic functions.</span> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="popup module3"> | |
| − | + | <span class="popuptext" id="module3"><b>Orthogonal site-specific proteases: </b><br/> A collection of orthogonal | |
| − | + | site-specific proteases that recognize different targets was prepared as split proteins, whose activity against | |
| − | + | selected targets can be induced by stimulation with an external signal such as light or chemicals.</span> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="popup module4"> | |
| − | + | <span class="popuptext" | |
| − | + | id="module4"> <b>Protease-triggered rapid secretion <br/> of therapeutic proteins:</b> <br/>A rapid cellular | |
| − | + | response by secretion of a protein is triggered by the proteolytic cleavage of an endoplasmic reticulum retention | |
| − | + | peptide. After the cleavage the cargo protein is moved from the ER, and secreted as therapeutic protein.</span> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | <div class="ui segment"> | |
| − | + | <h4><span id="experts" class="section colorize"> </span>Abstract for experts</h4> | |
| − | + | <p>Synthetic biology opens exciting perspectives to control cells, for applications ranging from | |
| − | + | industrial processes to cell-based therapy. However, the large majority of designed cellular | |
| − | + | circuits are based on transcriptional regulation, which may be too slow for many | |
| − | + | therapeutic or diagnostic applications, for example delivery of insulin or detection of a | |
| − | + | metabolite. Several medical doctors and researchers that we consulted stressed that a fast | |
| − | + | but controllable response is high on their wish list of expectations from synthetic biology. | |
| − | </div> | + | Additionally, noninvasive stimulation of selected tissues in the organism would also be |
| + | highly desirable. While light is extremely useful as a rapid, spatially-restricted input | ||
| + | signal, it cannot penetrate deep into the tissue. On the other hand, ultrasound combines | ||
| + | several advantages of light with the added ability to penetrate tissue.</p> | ||
| + | <p>In our project we enhanced the sensitivity of mammalian cells to ultrasound or other | ||
| + | mechanical stimuli by introduction of bacterial or engineered mammalian mechanosensors. | ||
| + | Additionally, the response to ultrasound and touch was strongly increased by expression of | ||
| + | the two components of bacterial gas vesicles, GvpA and GvpC. Mechanosensing was detected by | ||
| + | the calcium-induced calmodulin-M13 complex reconstituting split cyclic luciferase, highly | ||
| + | applicable for the emerging field of mechanogenetics. This enabled us to draw on cells using | ||
| + | touch, where we engaged in collaboration with the artist Laura Olalde.</p> | ||
| + | <p>For the rapid response of cells to multiple stimuli we designed proteolysis-based signaling | ||
| + | pathways. Four orthogonal split proteases were generated, each recognizing | ||
| + | its own motif of seven amino acid residues. Based on cleavage of coiled-coil dimerizing | ||
| + | domains we demonstrated the ability to implement proteolysis-based signal pathways and logic | ||
| + | functions in mammalian cells. Based on the cleavage of an ER retention peptide by a | ||
| + | protease, input signals led to protein secretion without the slow step of induced protein | ||
| + | synthesis.</p> | ||
| + | <p>We believe that this project introduced several foundational advances that could be very | ||
| + | useful to synthetic biology far beyond iGEM and for the benefit of humanity for therapy, | ||
| + | diagnostics and potentially many other advanced applications.</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="ui segment"> | ||
| + | <h4><span id="plain" class="section colorize"> </span>Abstract in plain English</h4> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | Synthetic biology aims to control cells so they can obey our commands and do what we want, | ||
| + | for example produce drugs when needed. In our project we made cells which respond to ultrasound | ||
| + | or touch. When we touch the cells they light up, which can be recorded on a camera. Ideally | ||
| + | we want cells to respond to our commands as fast as possible, because sometimes we can’t | ||
| + | wait an hour before the cells produce the medicine and release it. That is why we gave cells | ||
| + | a novel mechanism of processing information. | ||
| + | We achieved this by combining several enzymes that recognize very specific parts of proteins | ||
| + | and cut them, which changes their function. This allowed us to combine different signals, | ||
| + | like sound, touch, light or chemicals, to obtain the desired cell response. The new enzymes | ||
| + | can also cut the anchor with which medicines are attached to cells after the cells make | ||
| + | them. Among many possible uses of our inventions, we can imagine activating cells in the | ||
| + | brain by ultrasound, which means that we don’t need to use | ||
| + | surgery to help people with Parkinson’s disease, or can trigger fast production of insulin | ||
| + | in the body, to help people with diabetes. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | <h1 class="ui centered dividing header"><span id="achievements" class="section colorize"> </span>Achievements | ||
| + | </h1> | ||
| + | <div class="ui segment"> | ||
| + | <div class="corners" style="float:right;"> | ||
| + | <p><img src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"> new in science | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <p><img src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/0/0d/T--Slovenia--igemLogoSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="30" height="30" style="display: inline;"> new at iGEM</p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Mammalian cell sensitivity to ultrasound and mechanical stimuli was increased by | ||
| + | ectopic expression of bacterial or human cation permeable channels and functional | ||
| + | reconstitution of bacterial protein gas vesicles from two protein components (GvpA | ||
| + | and GvpC) <img src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>A custom-made ultrasound generator device was used to stimulate mammalian cells <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/0/0d/T--Slovenia--igemLogoSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="30" height="30" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>A mechano-sensory luciferase reporter sensitive to an influx of free calcium ions | ||
| + | was introduced into mammalian cells, which enabled rapid light emission of mammalian | ||
| + | cells in response to mechanical stimuli and enabled painting on cells by touch with | ||
| + | exciting potentials for other applications <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>A cyclic proteolysis-activated luciferase reporter was experimentally verified and | ||
| + | introduced into the iGEM collection <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/0/0d/T--Slovenia--igemLogoSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="30" height="30" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>A set of four different orthogonal site-specific proteases was designed and tested | ||
| + | as split proteins with induced reconstitution in mammalian cells <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>New orthogonal protease-based signaling pathways were designed as an information processing platform | ||
| + | and several logic functions based on the combination of multiple input | ||
| + | signals were tested experimentally <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | <li>Proteolysis of ER retention signal was introduced as the trigger for the fast | ||
| + | release of proteins from cells aimed to enable fast therapeutic responses such as | ||
| + | required for the release of peptide hormones, neuroactive peptides etc. <img | ||
| + | src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/d/dc/T--Slovenia--starSmall.png" | ||
| + | alt="newAtiGEM" width="28" height="28" style="display: inline;"></li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | <h1 class="ui centered dividing header"><span id="requirements" class="section colorize"> </span>Medal | ||
| + | requirements</h1> | ||
| + | <div class="ui basic segment"> | ||
| + | <table class="ui collapsing unstackable celled table" style="box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(34,36,38,.15)"> | ||
| + | <thead class="full-width"> | ||
| + | <tr class="center aligned"> | ||
| + | <th> Medal</th> | ||
| + | <th> Criteria</th> | ||
| + | <th> Explanation</th> | ||
| + | <th></th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </thead> | ||
| + | <tbody> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan="4" class="center aligned" style="background-color: gold">GOLD</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Integrated Human Practices</td> | ||
| + | <td>Expand on your silver medal activity by demonstrating how you have integrated | ||
| + | the investigated issues into | ||
| + | the design and/or execution of your project. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>Implementation of several <a | ||
| + | href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Integrated_Practices">experts from | ||
| + | different medical fields and culturologists</a> helped us | ||
| + | improve our | ||
| + | project. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Improve a previous part or project | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>Improve the function OR characterization of an existing BioBrick Part or Device | ||
| + | and enter this information | ||
| + | in the Registry. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>We <a href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Parts">improved</a> the parts | ||
| + | <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K737005:Experience">BBa_K737005</a> and <a | ||
| + | href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K157010:Experience">BBa_K157010</a> | ||
| + | by equipping them with additional tags, expressing them | ||
| + | in human cells and further characterizing their function. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Proof of concept</td> | ||
| + | <td>Demonstrate a functional proof of concept of your project. </td> | ||
| + | <td>We successfully demonstrated the functionality of selected (split) proteases and | ||
| + | used them to <a | ||
| + | href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Demonstrate">control | ||
| + | secretion</a> of the reporter protein from the cell. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Demonstrate your work</td> | ||
| + | <td>How your project works under real-world conditions. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>We showed that our mechanosensing constructs coexpressed in human cells allow | ||
| + | for a controlled response to | ||
| + | touch and used them for our art application, <a | ||
| + | href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Proof">Touch painting</a>. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan="4" class="center aligned" style="background-color: silver">SILVER</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Validated Part / Validated Contribution</td> | ||
| + | <td>Experimentally validate that at least one new BioBrick Part or Device of your | ||
| + | own design and construction | ||
| + | works as expected. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>We demonstrated the functionality of our constructs and provided experimental | ||
| + | data. We created a list of our | ||
| + | <a href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Parts">favorite parts</a> | ||
| + | and detailed our experiences with them. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Collaboration</td> | ||
| + | <td>Convince the judges you have helped any registered iGEM team from high school, a | ||
| + | different track, another | ||
| + | university, or another institution in a significant way. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>During our project we had several skype meetings with other iGEM teams. We also | ||
| + | provided iGEM Team biotINK | ||
| + | from Munich with <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K782063">BBa_K782063 | ||
| + | created by team Slovenia 2012.</a> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Human Practices</td> | ||
| + | <td>Demonstrate how your team has identified, investigated, and addressed one or | ||
| + | more of issues (education, | ||
| + | public engagement, public policy issues, public perception, or other activities) | ||
| + | in the context of your | ||
| + | project. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>Education and transmission of interest in science is an <a | ||
| + | href="https://2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/HP/Gold">important part of our | ||
| + | project</a>. This | ||
| + | is why we | ||
| + | prepared several lectures for high school students and also collaborated with an | ||
| + | artist who gave our project | ||
| + | a new perspective by conveying science to public through art. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td colspan="4" class="center aligned" style="background-color: #CD7F32">BRONZE</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Register and attend</td> | ||
| + | <td>Register for iGEM.</td> | ||
| + | <td>We have successfully registered.</td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Deliverables</td> | ||
| + | <td>Meet all deliverables on the Requirements page.</td> | ||
| + | <td>We met all the listed deliverables.</td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Attribution</td> | ||
| + | <td>Create a page on your team wiki with clear attribution of each aspect of your | ||
| + | project. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>We created a <a href="//2016.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/Attributions">wiki page</a> describing | ||
| + | the attributions to the | ||
| + | project. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Part / Contribution</td> | ||
| + | <td>Document at least one new standard BioBrick Part or Device central to your | ||
| + | project and submit this part to | ||
| + | the iGEM Registry. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td>We documented and submitted 52 standard <a | ||
| + | href="//parts.igem.org/cgi/partsdb/pgroup.cgi?pgroup=iGEM2016&group=Slovenia">BioBrick | ||
| + | parts</a>. | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td><i class="large green checkmark icon"></i></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </tbody> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | <a href="//igem.org/Main_Page"> | ||
| + | <img border="0" alt="iGEM" src="//2016.igem.org/wiki/images/8/84/T--Slovenia--logo_250x250.png" width="5%" style = "position: fixed; bottom:0%; right:1%;"> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <!-- Start of StatCounter Code for Default Guide --> | ||
| + | <script type="text/javascript"> | ||
| + | var sc_project=11075328; | ||
| + | var sc_invisible=1; | ||
| + | var sc_security="3aea03ab"; | ||
| + | var scJsHost = (("https:" == document.location.protocol) ? | ||
| + | "https://secure." : "http://www."); | ||
| + | document.write("<sc"+"ript type='text/javascript' src='" + | ||
| + | scJsHost+ | ||
| + | "statcounter.com/counter/counter.js'></"+"script>"); | ||
| + | </script> | ||
| + | <noscript><div class="statcounter"><a title="shopify | ||
| + | analytics ecommerce tracking" | ||
| + | href="http://statcounter.com/shopify/" target="_blank"><img | ||
| + | class="statcounter" | ||
| + | src="//c.statcounter.com/11075328/0/3aea03ab/1/" | ||
| + | alt="shopify analytics ecommerce | ||
| + | tracking"></a></div></noscript> | ||
| + | <!-- End of StatCounter Code for Default Guide --> | ||
</body> | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:50, 19 October 2016
Sonicell
For the therapy of diseases such as diabetes, we require a system of drug delivery that is fast, controllable and noninvasive. Engineering cells to produce drugs in the tissue is a promising direction. However, in most genetic circuits designed by synthetic biology the response is delayed due to the need to transcripe and translate the mediators. Project Sonicell introduces exciting foundational advances to synthetic biology aimed to enable rapid cellular response to a combination of external stimuli such as sound, light or chemical compounds. This system is composed of a module for enhanced sensitivity of cells to ultrasound or other mechanical stimuli, sensed by a calcium-dependent reporter, and a module for integration of a combination of several input signals into a signaling pathway based on proteolysis by a collection of orthogonal proteases. Finally, the proteases were designed to cleave an endoplasmic reticulum retention signal from target proteins, which results in secretion of premade proteins.
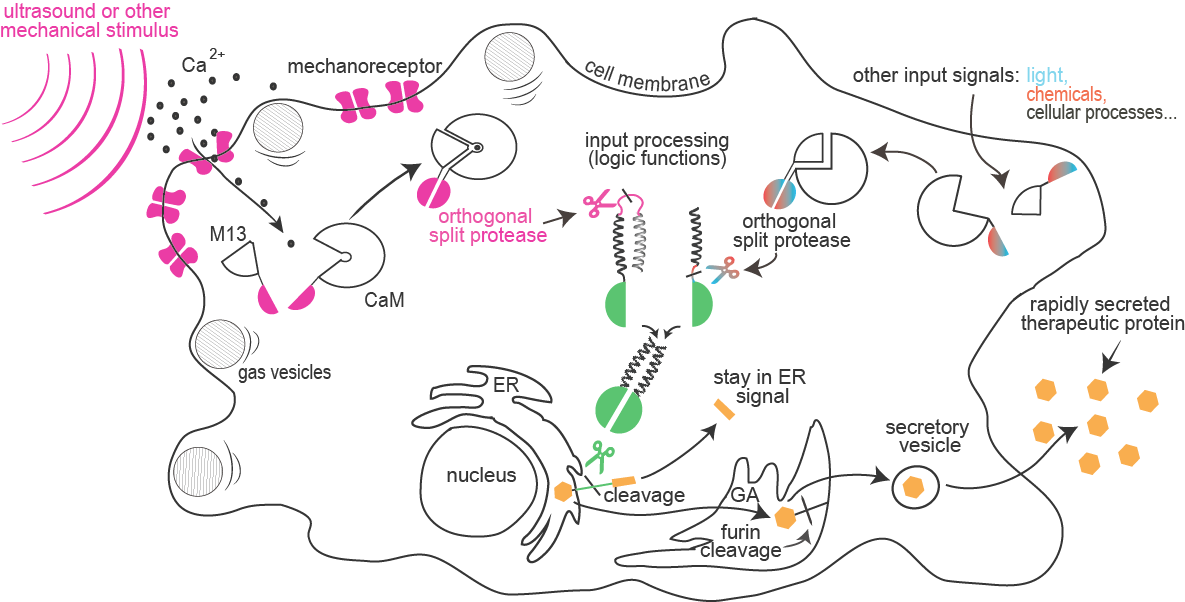
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to ultrasound or other mechanical stimuli was enhanced by the introduction of mechanosensitive ion channels and/or by the expression of protein gas vesicles from bacteria. Influx of calcium through channels is sensed by formation of a complex between calmodulin and M13 peptide that can result in a rapid light emission by cells (used for cell painting) or reconstitution of a split protease.
and information processing:
Combinations of proteolytic activities against specific targets resulted in activation of a reporter or another protease, which forms the basis for the design of a new type of rapid signaling pathways and construction of logic functions.
A collection of orthogonal site-specific proteases that recognize different targets was prepared as split proteins, whose activity against selected targets can be induced by stimulation with an external signal such as light or chemicals.
of therapeutic proteins:
A rapid cellular response by secretion of a protein is triggered by the proteolytic cleavage of an endoplasmic reticulum retention peptide. After the cleavage the cargo protein is moved from the ER, and secreted as therapeutic protein.
Abstract for experts
Synthetic biology opens exciting perspectives to control cells, for applications ranging from industrial processes to cell-based therapy. However, the large majority of designed cellular circuits are based on transcriptional regulation, which may be too slow for many therapeutic or diagnostic applications, for example delivery of insulin or detection of a metabolite. Several medical doctors and researchers that we consulted stressed that a fast but controllable response is high on their wish list of expectations from synthetic biology. Additionally, noninvasive stimulation of selected tissues in the organism would also be highly desirable. While light is extremely useful as a rapid, spatially-restricted input signal, it cannot penetrate deep into the tissue. On the other hand, ultrasound combines several advantages of light with the added ability to penetrate tissue.
In our project we enhanced the sensitivity of mammalian cells to ultrasound or other mechanical stimuli by introduction of bacterial or engineered mammalian mechanosensors. Additionally, the response to ultrasound and touch was strongly increased by expression of the two components of bacterial gas vesicles, GvpA and GvpC. Mechanosensing was detected by the calcium-induced calmodulin-M13 complex reconstituting split cyclic luciferase, highly applicable for the emerging field of mechanogenetics. This enabled us to draw on cells using touch, where we engaged in collaboration with the artist Laura Olalde.
For the rapid response of cells to multiple stimuli we designed proteolysis-based signaling pathways. Four orthogonal split proteases were generated, each recognizing its own motif of seven amino acid residues. Based on cleavage of coiled-coil dimerizing domains we demonstrated the ability to implement proteolysis-based signal pathways and logic functions in mammalian cells. Based on the cleavage of an ER retention peptide by a protease, input signals led to protein secretion without the slow step of induced protein synthesis.
We believe that this project introduced several foundational advances that could be very useful to synthetic biology far beyond iGEM and for the benefit of humanity for therapy, diagnostics and potentially many other advanced applications.
Abstract in plain English
Synthetic biology aims to control cells so they can obey our commands and do what we want, for example produce drugs when needed. In our project we made cells which respond to ultrasound or touch. When we touch the cells they light up, which can be recorded on a camera. Ideally we want cells to respond to our commands as fast as possible, because sometimes we can’t wait an hour before the cells produce the medicine and release it. That is why we gave cells a novel mechanism of processing information. We achieved this by combining several enzymes that recognize very specific parts of proteins and cut them, which changes their function. This allowed us to combine different signals, like sound, touch, light or chemicals, to obtain the desired cell response. The new enzymes can also cut the anchor with which medicines are attached to cells after the cells make them. Among many possible uses of our inventions, we can imagine activating cells in the brain by ultrasound, which means that we don’t need to use surgery to help people with Parkinson’s disease, or can trigger fast production of insulin in the body, to help people with diabetes.
Achievements
![]() new in science
new in science
![]() new at iGEM
new at iGEM
- Mammalian cell sensitivity to ultrasound and mechanical stimuli was increased by
ectopic expression of bacterial or human cation permeable channels and functional
reconstitution of bacterial protein gas vesicles from two protein components (GvpA
and GvpC)

- A custom-made ultrasound generator device was used to stimulate mammalian cells

- A mechano-sensory luciferase reporter sensitive to an influx of free calcium ions
was introduced into mammalian cells, which enabled rapid light emission of mammalian
cells in response to mechanical stimuli and enabled painting on cells by touch with
exciting potentials for other applications

- A cyclic proteolysis-activated luciferase reporter was experimentally verified and
introduced into the iGEM collection

- A set of four different orthogonal site-specific proteases was designed and tested
as split proteins with induced reconstitution in mammalian cells

- New orthogonal protease-based signaling pathways were designed as an information processing platform
and several logic functions based on the combination of multiple input
signals were tested experimentally

- Proteolysis of ER retention signal was introduced as the trigger for the fast
release of proteins from cells aimed to enable fast therapeutic responses such as
required for the release of peptide hormones, neuroactive peptides etc.

Medal requirements
| Medal | Criteria | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOLD | |||
| Integrated Human Practices | Expand on your silver medal activity by demonstrating how you have integrated the investigated issues into the design and/or execution of your project. | Implementation of several experts from different medical fields and culturologists helped us improve our project. | |
| Improve a previous part or project | Improve the function OR characterization of an existing BioBrick Part or Device and enter this information in the Registry. | We improved the parts BBa_K737005 and BBa_K157010 by equipping them with additional tags, expressing them in human cells and further characterizing their function. | |
| Proof of concept | Demonstrate a functional proof of concept of your project. | We successfully demonstrated the functionality of selected (split) proteases and used them to control secretion of the reporter protein from the cell. | |
| Demonstrate your work | How your project works under real-world conditions. | We showed that our mechanosensing constructs coexpressed in human cells allow for a controlled response to touch and used them for our art application, Touch painting. | |
| SILVER | |||
| Validated Part / Validated Contribution | Experimentally validate that at least one new BioBrick Part or Device of your own design and construction works as expected. | We demonstrated the functionality of our constructs and provided experimental data. We created a list of our favorite parts and detailed our experiences with them. | |
| Collaboration | Convince the judges you have helped any registered iGEM team from high school, a different track, another university, or another institution in a significant way. | During our project we had several skype meetings with other iGEM teams. We also provided iGEM Team biotINK from Munich with BBa_K782063 created by team Slovenia 2012. | |
| Human Practices | Demonstrate how your team has identified, investigated, and addressed one or more of issues (education, public engagement, public policy issues, public perception, or other activities) in the context of your project. | Education and transmission of interest in science is an important part of our project. This is why we prepared several lectures for high school students and also collaborated with an artist who gave our project a new perspective by conveying science to public through art. | |
| BRONZE | |||
| Register and attend | Register for iGEM. | We have successfully registered. | |
| Deliverables | Meet all deliverables on the Requirements page. | We met all the listed deliverables. | |
| Attribution | Create a page on your team wiki with clear attribution of each aspect of your project. | We created a wiki page describing the attributions to the project. | |
| Part / Contribution | Document at least one new standard BioBrick Part or Device central to your project and submit this part to the iGEM Registry. | We documented and submitted 52 standard BioBrick parts. | |




