(Prototype team page) |
|||
| (53 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{UCL}} | + | {{UCL/TemplateBefore}} |
| + | |||
<html> | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <main class="cd-main-content"> | ||
| + | <div id="main-content-container ess-menu-bgd-prettify-blue"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="ess-template-page"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="background-image: url('https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/9/9d/T--UCL--lab2.png'); background-position: 50% 0;" | ||
| + | class="ess-template-fixed-bgd-section"> | ||
| + | <div class="container" style="height: 250px;"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-md-12 text-center animate-box" style="margin-top: 5em;"> | ||
| + | <h1 style="color: white; font-weight: 600;">RESULTS</h1> | ||
| + | <h3 style="color: white;">Final experimental data</h3> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-md-12" style="padding-top: 45px"> | ||
| + | <div style="text-align: center"> | ||
| + | <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/6/63/T--UCL--swirl.png" width="190" height="90"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="ess-template-general-section" style="color: black;"> | ||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2 ess-template-general animate-box"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2> <center> GOLD MEDAL: irrE BioBrick enables E. coli to persist in medical lubricant </center> | ||
| + | </h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/36/T--UCL--irregraph.png"> </center> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <p> Diagram to show different growth of wild type E.coli vs. IrrE E.coli in 40% Lubricant 60% LB using Absorbance at 600nm </p> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> From the data shown in the graph above it clearly shown that the E.Coli transformed with IrrE grows better in the 40%Lubricant/60%LB solution in direct comparison with the Wild type E.Coli, which hardly grew at all. This data thus suggests that with the IrrE the E.Coli is better adapted to living in, which would allow further studies being conducted on the maximum concentration of Lubricant it can be grown in. Furthermore once that has been determined the pathogen detecting aspect of the concept can be realised. | ||
| + | Thus overall this experiment has allowed us to show that IrrE increases the growth of the E. Coli in the Superdrug Lubricant containing: purified water, glycerine, Carbopol 940, Triethanolamine and Sodium Butyl Paraben. This supports the previous experiments that concluded that IrrE allows for better growth in saline conditions[iv], except this time in Superdrug Lubricant. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> For further conceptualisation and experimentation it should be taken into consideration that within a commercialisable product the bacteria will not be under ideal growth conditions and the nutrients will be a limiting factor, especially when considering that the lubricant concentration will have to be a lot higher than in this experiment.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="row"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2 ess-template-general animate-box"> | ||
| + | <h2> <center> SILVER: Lycopene BioBrick </center> </h2> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <h3> <center> mNARK-Lycopene Device Characterisation </center> </h3> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/8/83/T--UCL--hypoxiadata.png"> </center> | ||
| + | <p> mNARK lycopene enables ecoli growth under Hypoxia conditions </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> Hypoxia is a condition in which cells are deprived of oxygen due to low concentration of oxygen in the extracellular milieu. In humans, low oxygen levels in the blood affect tissues. Oxygen is essential for diverse cellular functions, such as catabolic and anabolic processes, and low intracellular concentrations have a negative impact on cell functions and survival. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> Oxygen deficit can have a severe impact on cellular function, as seen in cell stress. The inability of cells to effectively manage cellular stress over time has been linked to cellular ageing and age-related diseases (Haigis and Yankner, 2010; Poljšak and Milisav, 2012). Cellular stress leads to deregulation of intracellular processes, as both the structure and function of macromolecules are compromised. Furthermore, high amounts of ROS have been implicated in cellular stress and ageing (Poljšak and Milisav, 2012). </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> We performed an additional assay expressing lycopene under the mNARK promoter, to test if the cells could survive longer under hypoxia-induced stress. E. coli cells transformed with this construct were compared with the wild type TOP10 E. coli (W/T) monitoring growth and division via optical density (OD) at 600 nm, at specific time points – 3 hours and 16 hours following withdrawal of oxygen. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> mNARK-Lycopene cells had a higher OD compared to the wild type cells. Cells exposed to hypoxia were also compared with the cells that were grown with oxygen. Most cells still survived despite the presence of hypoxia. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> Furthermore, with regards to W/T cells, a depletion in the oxygen concentration caused a drop in cell growth and division, as reflected in decreased OD measurements. However, growth and division of mNARK-Lyco-containing cells was maintained in oxygen-deficient environment during the 16-hour time test period. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> This shows that our BioBrick construct (mNARK-Lyco) was able to ensure cell growth and division in oxygen-deficient environment. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> The mNARK-Lycopene device is induced by oxidative stress and produces lycopene as means to 'mop up' the oxidative stress in the environment, in the form of a probiotic. </p> | ||
| + | <p>Under various stresses, the mNARK-Lycopene device promotes E. coli growth. Characterisation was achieved by comparing the performance of the BioBrick against wild type E. coli. </p> | ||
| + | <p>Initially, the growth of mNARK-Lycopene was compared with the growth of wild type E. coli. The mNARK-Lycopene cells substantially outperformed the wild type cells, reaching a final OD600 of around 0.45 and, potentially, still rising, while the growth of the wild type cells had clearly levelled off over the equivalent time period and had began to die, reaching a final OD600 of around 0.12. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/32/T--UCL--MichelleM-NarkGraph1.png"> </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>After carrying out the positive control, the mNARK-Lycopene cells were tested under conditions of simulated oxidative stress, with the LB media containing 2 mM copper (II) chloride. The results indicate that the mNARK-Lycopene device boots E. coli growth. Wild type E. coli grew to a final optical density of 0.35 after three hours, from an initial OD of 0.15. The mNARK-Lycopene progressed from an initial OD of 0.25 to a final OD of 0.60. </p> | ||
| + | <p>The BioBrick was then tested against simulated oxidative stress conditions of 50 and 100 µM sodium nitroprusside. Both of these experiments, again, indicate that, in the presence of simulate oxidative stress conditions, the mNARK-Lycopene promotes E. coli growth substantially better then the control. At 50 µM, the optical density of the wild type cells decreases to an OD of 0.05 from the initial reading of 0.17. In comparison, the mNARK-Lycopene cells achieved a final optical density of 0.33 from a low of 0.05. At the 100 µM concentration, the wild type cells flat lined, remaining at an optical density of 0.25, while the lycopene cell concentration increased substantially from an optical density of 0.07 to 0.45 after four hours of growth. </p> | ||
| + | <p> In summary, out analysis has shows that our mNARK-Lycopene device protects the cells from oxidative stress and, from this, we can assume that this effect will continue once our lycopene probiotic is consumed by and aging person. Additionally, it has been proved that the cells will be able to survive and multiply in the gut and colonise it. Therefore providing protection to neighbouring cells by ‘mopping up’ the oxidative stress. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/1/19/T--UCL--MichelleM-NarkGraph2.png"> </center> | ||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/33/T--UCL--MichelleM-NarkGraph3.png"> </center> | ||
| + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/3b/T--UCL--MichelleM-NarkGrapp.png"> </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> After establishing that the mNARK-Lycopene device improves cells growth compared to wild type E. coli, the growth of the Lycopene cells was measured against lycopene expression. </p> | ||
| + | <p> First, the cells were grown in LB media with 2 mM copper (II) sulphate. As shown in the plot, the mNARK-Lycopene device reached a higher cell density of 0.57, which corresponds to an OD485 of 0.68. Wild type E. coli does not achieve such a cell density and, by extension, lycopene expression. From an initial cell density of 0.08, the wild type cells reach a maximum cell density of 0.34. Additionally, the gradient of the graph represents the rate at which cells express lycopene. The plot indicates that the mNARK-Lycopene device expresses lycopene at a higher rate than the wild type cells. It is clear that, for both the mNARK-Lycopene device and wild type E. coli cells, lycopene expression increases with cell density, as more lycopene is being produced as a result of there being a larger number of lycopene producing cells. Therefore, it can be concluded that the mNARK-Lycopene mops up the oxidative stress, which prevents the cells from dying. Therefore allowing cells to grow to a greater optical density, and, as mentioned above, greater cell density corresponds with greater lycopene production. </p> | ||
| − | < | + | <p> The second graph is derived from experiments using LB with two different concentrations of sodium nitroprusside (SNP): 50 μM and 100 μM. During the experiment with 2 mM copper (II) sulphate; the wild type E. coli cells continue to grow, since it did not produce an environment where there was substantial oxidative stress. Sodium nitroprusside can create an environment with greater oxidative stress. Due to the greater oxidative stress, the wild type cells are unable to grow in these conditions and show a very low optical density at 485 nm, which indicates a lack of lycopene production. The gradient of the two wild type cell graphs are similar, which is expected, as neither have an oxidative stress promoter. Wild type cells grew better under less oxidative stress (50 μM SNP), compared to 100 μM SNP. The optical density at 485 nm is lower for higher oxidative stress conditions with the wild type cells, which is due to their respective cell densities. However, the mNARK-Lycopene cells continue to grow and produce lycopene in these conditions. The lycopene cells display greater growth in the harsher 100 μM conditions compared with 50 μM. The gradient of 50 μM mNARK-Lycopene at 0.8435 is less than that of the 100 μM sample, which is 1.0864. This indicates that our mNARK device increases lycopene expression under higher oxidative stress. In this experiment, the performance of the Lycopene cells is more pronounced, clearly showing that the mNARK-Lycopene devlice mops up the oxidative stress, which prevents the cells from dying. This results in a greater optical density being achieved and, by extension, greater lycopene production. </p> |
| + | <p> From the above data, we can deduce that our biobrick will produce more lycopene when there is more oxidative stress in older people there creating a regulatory feedback system. </p> | ||
| + | <p> Hence, we have characterised our silver BioBrick. </p> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <centre> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/a/a7/T--UCL--Lycopene2.jpg" > </centre> | ||
| + | <centre> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/c/c7/T--UCL--Lycopene1.jpg" > </centre> | ||
| − | + | </br> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | </ | + | |
| − | < | + | <div class="row"> |
| + | <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2 ess-template-general animate-box"> | ||
| + | |||
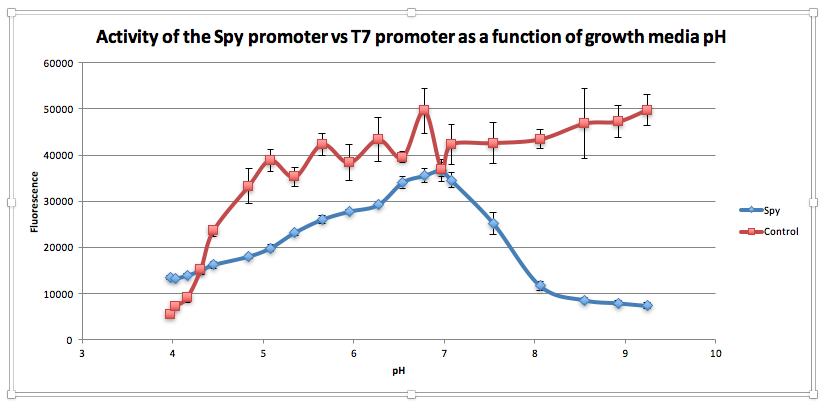
| + | <h2> <center>GOLD MEDAL: Spy promoter BioBrick functions as pH switch </center> </h2> | ||
| + | <p>The deterioration of oral health in the elderly is accompanied by an increased prevalence of caries and periodontal disease, which are risk factors for some systemic diseases and nutrition problems (1). | ||
| + | The oral cavity is inhabited by a wide range of interacting communities of metabolically and structurally organized microorganisms which synthesize an extracellular polysaccharide matrix (EPS) enabling them to adhere to the surface of the teeth and assemble in matrix-embedded biofilms. Progressing biofilm accumulation puts the bacteria under increasing metabolic stress, which leads to localized metabolite and acid accumulation and a shift in the dynamic homeostasis towards acid-tolerating species such as Gram-positive <span style="font-style: italic;">Streptococcus mutans</span> (3). A resultant decrease in pH causes tooth demineralization and constitutes a mechanism of dental caries. </p><br> | ||
| + | <p>In our project, we designed a biosynthetic device to serve as an alternative in preventative dental care for the elderly. We decided to target pH and an indicator of deteriorating oral health and use it as an system to regulate the relate of antimicrobial peptide known as mutacin III, is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria implicated in dental caries, e.g. other strains of <span style="font-style: italic;">Streptococcus mutans</span> and <span style="font-style: italic;">Actinomyces naeslundii</span>, while Gram-negative bacteria are resistant to inhibition (5).</p> <br> | ||
| + | <p>An existing BioBrick in the iGEM registry (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K239001">BBa_K239001</a>), designed to detect misfolding of proteins in the periplasm or shear stress has been further characterised to demonstrate the BioBrick functions as a pH inverter. </p> | ||
| − | < | + | <center><img src="/wiki/images/1/11/Spy_promoter.png" width="800" height="393"></center> |
| + | <p>Compared to the control, as pH increases from 3.97 to 6.78, GFP expression gradually increases for <span style="font-style: italic;">E. coli</span>with <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K239009">BBa_K239009</a>. The maximum GFP expression is observed at 6.78. GFP expression increases from 13,556.25 at pH 3.97 to 35,569 at pH 6.78. Beyond this maximum, there is a sharp decline in GFP expression as the starting LB broth increases in alkalinity, falling to 7,394 at pH 7,394. Conversely, for the control, a sharp increase is observed from pH 5393.5 at 3.97 to 38854.5 at pH 5.08. After this, the general trend is one of increasing fluorescence as pH increases, but the increase is more gradual.</p><br> | ||
| − | < | + | <p>From this experiment, we have established that <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K239009">BBa_K239009</a> (Spy Promoter) previously used to characterise protein misfolding can be used as a pH-sensitive promoter, as well. Thus, we have improved the function and characterization of an existing BioBrick Part.</p> |
| − | < | + | </div> |
| + | </div> | ||
| − | < | + | <div class="row"> |
| − | < | + | <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2 ess-template-general animate-box"> |
| − | < | + | <h2> <center> Superoxide Dismutase 3 Biobrick: GFP titration experiment </center> </h2> |
| − | </ | + | <center> <img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/8/81/T--UCL--SOD3data.png"> </center> |
| + | <h4> This data shows that as we increase the volume of lentivirus added to our lentivirus, there is an increase in the number of positive cells that have taken up the GFP construct. This data just confirms that lentivirus successfully transfects the gene of interest into our hela cells. </h4> | ||
| − | < | + | <div class="row"> |
| + | <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2 ess-template-general animate-box"><h3> <center> References </center> </h3> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li> Gil-Montoya JA, de Mello ALF, Barrios R, Gonzalez-Moles MA, Bravo M. Oral health in the elderly patient and its impact on general well-being: a nonsystematic review. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:461–7. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Rouxel P, Tsakos G, Chandola T, Watt RG. Oral Health-A Neglected Aspect of Subjective Well-Being in Later Life. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2016 Mar 12. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Anderson MH. Changing paradigms in caries management. Curr Opin Dent. 1992 Mar;2:157–62.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Qi F, Chen P, Caufield PW. Purification of mutacin III from group III <span style="font-style: italic;">Streptococcus mutans</span> UA787 and genetic analyses of mutacin III biosynthesis genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999 Sep;65(9):3880–7. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Hillman JD, Johnson KP, Yaphe BI. Isolation of a <span style="font-style: italic;">Streptococcus mutans</span> strain producing a novel bacteriocin. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):141–4.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Food Microbiology: Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Oct;3(10):777–88. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Bacterial lantibiotics: strategies to improve therapeutic potential. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2005 Feb;6(1):61–75.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Sahl HG, Jack RW, Bierbaum G. Biosynthesis and biological activities of lantibiotics with unique post-translational modifications. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jun 15;230(3):827–53.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Moll GN, Roberts GC, Konings WN, Driessen AJ. Mechanism of lantibiotic-induced pore-formation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1996 Feb;69(2):185–91</li> | ||
| + | <li>Smith L, Zachariah C, Thirumoorthy R, Rocca J, Novák J, Hillman JD, et al. Structure and dynamics of the lantibiotic mutacin 1140. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2003 Sep 9;42(35):10372–84. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Abee T. Pore-forming bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria and self-protection mechanisms of producer organisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 Jun 1;129(1):1–9.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Saising J, Dube L, Ziebandt A-K, Voravuthikunchai SP, Nega M, Gotz F. Activity of Gallidermin on Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Nov 1;56(11):5804–10.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Draper LA, Cotter PD, Hill C, Ross RP. Lantibiotic Resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015 Jun;79(2):171–91. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Hagiwara A, Imai N, Nakashima H, Toda Y, Kawabe M, Furukawa F, et al. A 90-day oral toxicity study of nisin A, an anti-microbial peptide derived from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010 Aug;48(8-9):2421–8. </li> | ||
| + | <li>Delves-Broughton J. Nisin and its application as a food preservative. Int J Dairy Technol. 1990 Aug;43(3):73–6. </li> | ||
| − | < | + | </ol> |
| + | </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </div> | + | </div> |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </main> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| + | {{UCL/TemplateAfter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 20 October 2016
<!DOCTYPE html>