Sandra Youpi (Talk | contribs) |
Sandra Youpi (Talk | contribs) (→Proof of fonctionnality) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=== Proof of fonctionnality=== | === Proof of fonctionnality=== | ||
We investigated if DesA (Lysine decarboxylase) was fonctionnal by measurement of cadaverine using HPLC with C18 column and we proved that our biobrick allows the production of DesA which enables to produce the cadaverine and makes it fonctionnal. | We investigated if DesA (Lysine decarboxylase) was fonctionnal by measurement of cadaverine using HPLC with C18 column and we proved that our biobrick allows the production of DesA which enables to produce the cadaverine and makes it fonctionnal. | ||
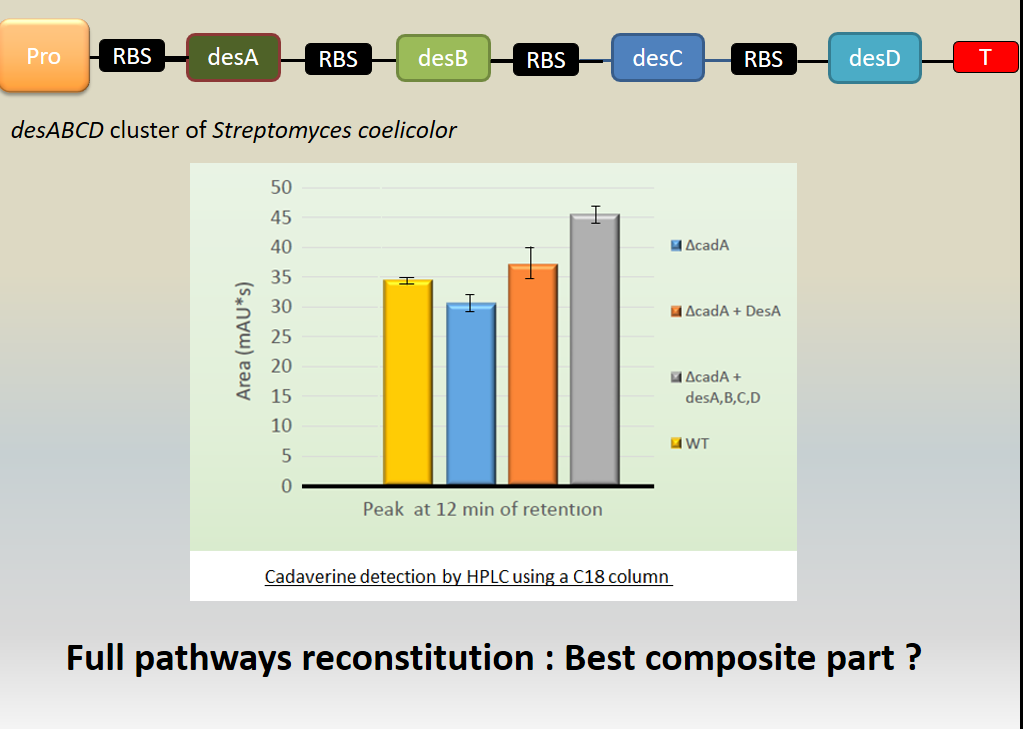
| − | [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--result5.jpeg|500px|tight|thumb| Investigation of the cadaverine production by the lysine decarboxylase DesA. The cadaverin production has been detected by HPLC using C18 column after induction of the <i>des</i> genes. Different backgrounds were analysed : wild type <i>Escherichia coli</i> TG1 strain (yellow column), <i>cadA</i> mutant from Keio bank (blue column), complemented <i> cadA </i> mutant from Keio bank with p<i>cadA</i> ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951004 Bba_K1951004])(orange column), complemented <i>cadA</i> mutant from Keio bank with <i>des</i> operon ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 Bba_K1951011])(grey column).]] | + | [[File:T--Aix-Marseille--result5.jpeg|500px|tight|thumb| Investigation of the cadaverine production by the lysine decarboxylase DesA. The cadaverin production has been detected by HPLC using C18 column after induction of the <i>des</i> genes. Different backgrounds were analysed : wild type <i>Escherichia coli</i> TG1 strain (yellow column), <i>cadA</i> mutant from Keio bank (blue column), complemented <i> cadA </i> mutant from Keio bank with p<i>cadA</i> ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951004 Bba_K1951004]) (orange column), complemented <i>cadA</i> mutant from Keio bank with <i>des</i> operon ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 Bba_K1951011]) (grey column).]] |
Results showed cadaverine detection in the wild type meaning the original strain well produces the cadaverine. | Results showed cadaverine detection in the wild type meaning the original strain well produces the cadaverine. | ||
| − | In cadA mutant from Keio bank, cadaverine was also produced in a least quantity showing that an other pathway is responsible for the production of cadaverine ( existence of an other constitutive lysine decarboxylase in the <i> E. coli </i> genome. | + | In <i>cadA</i> mutant from Keio bank, cadaverine was also produced in a least quantity showing that an other pathway is responsible for the production of cadaverine (existence of an other constitutive lysine decarboxylase in the <i> E. coli </i> genome. |
| − | In the cadA mutant complemented by Bba_K1951004, the amount of cadaverine was recovered and even beyond the wild type production. | + | In the <i>cadA</i> mutant complemented by p<i>cadA</i> ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951004 Bba_K1951004]), the amount of cadaverine was recovered and even beyond the wild type production. |
| − | Moreover, in the cadA mutant complemented by Bba_K1951011, the cadaverine level produced was even over the wild type and complemented Bba_K1951004 production. We explain this result because of the higher stability of this big composite part. | + | Moreover, in the <i>cadA</i> mutant complemented by the des operon ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 Bba_K1951011]), the cadaverine level produced was even over the wild type and complemented Bba_K1951004 production. We explain this result because of the higher stability of this big composite part. |
To conclude, we made a big composite part able to produce every proteins involved in the biosynthetic pathway of the desferrioxamine B. | To conclude, we made a big composite part able to produce every proteins involved in the biosynthetic pathway of the desferrioxamine B. | ||
Results
Our lab experience enabled us to create the final Biobricks of our project which are a siderophore Desferrioxamine B producer and a flagellin producer.
Mobilisation results
Protein production
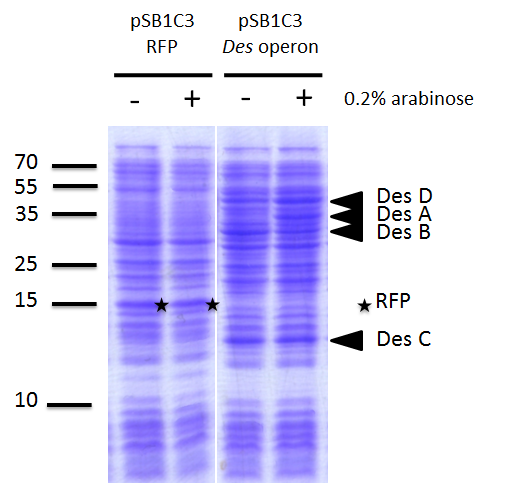
We investigated if the DesA, DesB, DesC and DesD proteins were well produced by our biobrick [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 BBa_K1951011] using SDS PAGE.
To do this we performed SDS PAGE (protocol) and stained with coomassie blue using cells containing this biobrick. From an over night starter, cells were diluted and grown from Abs(600nm)=0.2 to Abs(600nm)=1. Then 1UOD of cells (1.67ml at 0.6OD) was collected and centrifuged at 5000g for 5min. After removal of the supernatant, the cell pellet was resuspended in 50µL SDS-PAGE sample buffer. We heated the mix at 95°C during 15min. The sample was loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel and migrated during 50min at 180V. Staining was done using coomassie blue.
We compared the production of proteins in different background :
- E. coli TG1 strain with pSB1C3 containing the RFP coding sequence (negative control)
- E. coli TG1 strain with des operon ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 BBa_K1951011]) before and after induction. (You can observe the production of the 4 proteins on the figure on the right; left : before induction, right : after induction)
Results showed the production of the 4 proteins DesA, DesB, DesC and DesD, all involved in the desferrioxamine B biosynthesis pathway.
Proof of fonctionnality
We investigated if DesA (Lysine decarboxylase) was fonctionnal by measurement of cadaverine using HPLC with C18 column and we proved that our biobrick allows the production of DesA which enables to produce the cadaverine and makes it fonctionnal.
Results showed cadaverine detection in the wild type meaning the original strain well produces the cadaverine.
In cadA mutant from Keio bank, cadaverine was also produced in a least quantity showing that an other pathway is responsible for the production of cadaverine (existence of an other constitutive lysine decarboxylase in the E. coli genome.
In the cadA mutant complemented by pcadA ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951004 Bba_K1951004]), the amount of cadaverine was recovered and even beyond the wild type production.
Moreover, in the cadA mutant complemented by the des operon ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1951011 Bba_K1951011]), the cadaverine level produced was even over the wild type and complemented Bba_K1951004 production. We explain this result because of the higher stability of this big composite part.
To conclude, we made a big composite part able to produce every proteins involved in the biosynthetic pathway of the desferrioxamine B.
In the futur
- Test the whole pathway
- siderophore production (HPLC and absorption spectroscopy)
- Improve the siderophore production if needed (cofactors, protein stability, metabolic engineering)
- Binding affinity for platinum by our siderophore
- ICPAES (ion coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy)
- Importation of the siderophore in Streptomyces coelicolor
Biosorption result
Proof of protein production
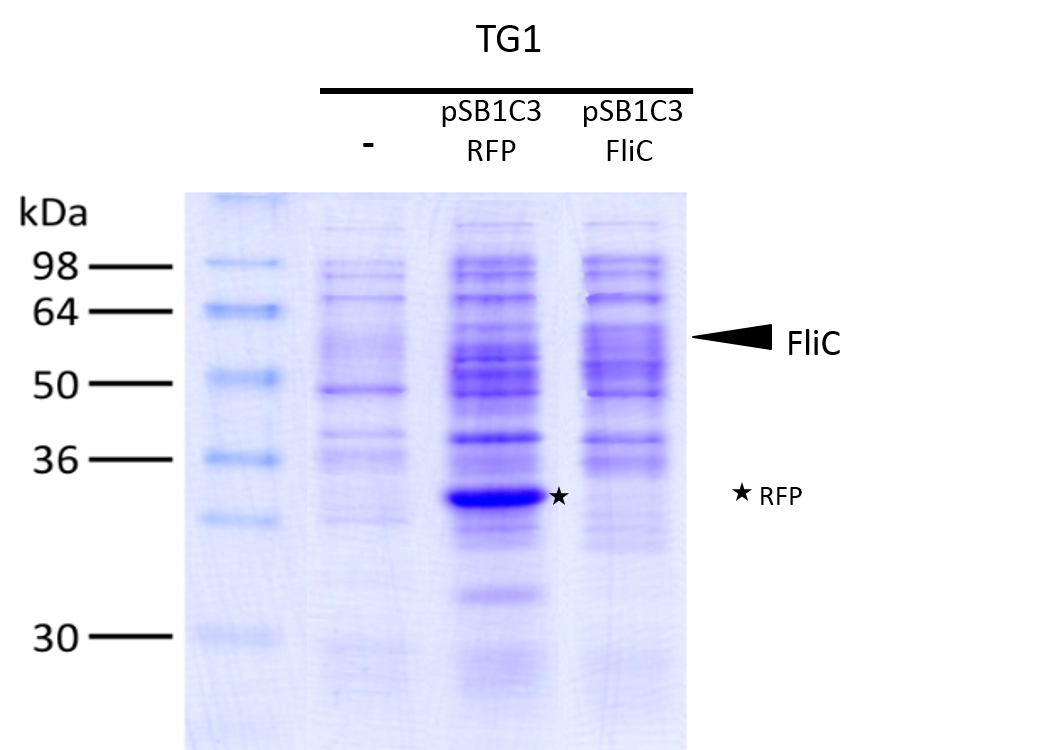
We investigated if the FliC protein was well produced by our biobrick using SDS PAGE.
To to do this we performed SDS PAGE and stained with coomassie blue using cells containing this biobrick in plasmid backbone SDS page and coomassie blue.
From an over night starter, cells were diluted and grown from Abs(600nm)=0.2 to Abs(600nm)=0.6.
Then 1UOD of cells (1.67ml at 0.6OD) was collected and centrifuged at 5000g for 5min.
After removal of the supernatant, the cell pellet was resuspended in 50µL SDS-PAGE sample buffer.
SDS page and coomassie blue The mixture was loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel and migrated during 50min at 180V.
Staining was done using coomassie blue.
The FliC is at mass 51,3kDa, and can be clearly seen in the gel photograph.
Proof of swimming recovery
We have made a biobrick BbaK1951008 ables to produce Flagellin (FliC protein of the flagellum). In the aim to test the flagellin integrity, we made a fliC mutant in a E. coli W3110 strain by transduction using phage P1 (protocol available on our website).
In the figure the deletion mutant (lower left sector) shows no swimming motility as expected and a small white colony.
In contrast the wild-type colony (lower right) has a diffuse halo due to swimming cells around the central white colony.
Finally the complemented strain, the deletion mutant complemented with our biobrick, (top panel) shows two colonies with intense
halos surrounding them.
This illustrated clearly that our biobrick can restore motility and is functional.
The intensity of the halo suggests that a greater proportion of the cells are mobile or swimming is in someway better than the wild-type.
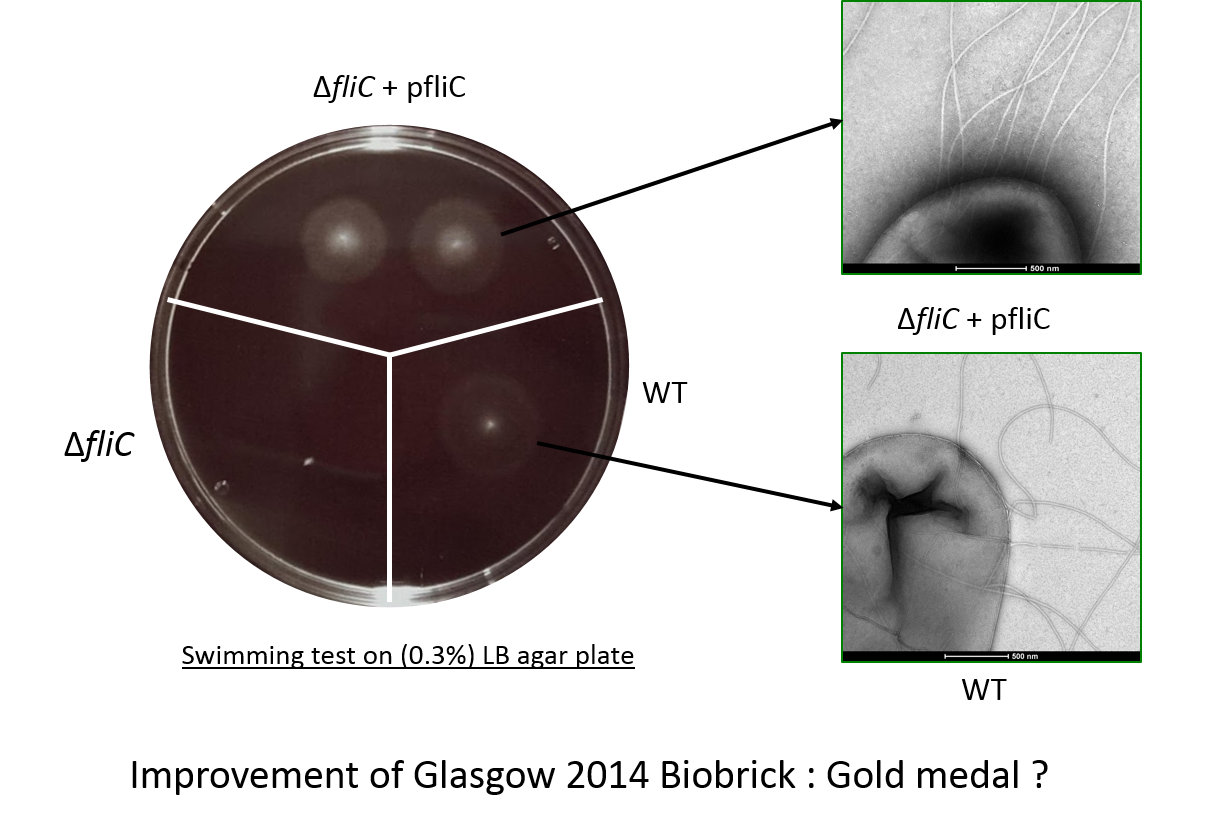
Electron microscopy of the flagella
This check the flagella assembly and the integration of the flagellin protein expressed from our biobrick BBa_K1951008 we have observed bacteria with an electron microscope.
The image shows mutiple polar flagella in an E. coli fliC deletion mutant containing our biobrick. We saw that these cells had more flagella than wild-type (W3110) cells and that the fliC deletion mutant did not have flagella.
In the futur
- Adsorption of platinum by our flagella
- election microscopy observation
- Finalise the insertion of platinum specific peptide
- directed mutagenesis introducing a Bbs1 restriction site
- insertion by annealing
- Metal recovery by calcination or proteolysis
- Extend to other precious metals (other peptides : gold, silver, palladium)
Improvement of FliC E. coli [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1463604 BBa_K1463604]
This biobrick is an improvement on the biobrick designed by the Glasgow 2014 team. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1463604 K1463604]
The improvement of this part is multiple.
- First there is no mutation in the promotor or RBS of our part so the flagellin is well expressed and functional. Unfortunately when the Glasgow team trie to make this part they picked up a mutation in the promotor.
- Second the sequence that we have used it a synthetic gene with codon optimisation, designed specifically for high level expression in E. coli. Thus as an expression part is improved over the initial design.
- Third in the functional swimming assay, we see evidence for improved swimming (denser halo), in cells expressing our biobrick, a phenotype not observed by the Glasgow team in 2014.
Futur plan for our project
Now that every biobricks have been created and are available, make proofs of concept could allow to envisage investigation about possibilities of an industrial application.
The biologic production of high and specific adsorber could reduce environnemental impact of the metal production and its cost while renew essential precious metals like platinum, for a sustainable production.