m (→Nanoparticles) |
m (→Nanoparticles) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Some platinum prices estimations have been made relying in available prices in websites. Let's consider the 780 mg produced in the final step are available at the end of the further purification steps : | Some platinum prices estimations have been made relying in available prices in websites. Let's consider the 780 mg produced in the final step are available at the end of the further purification steps : | ||
| − | -200 nm sized nanparticles ([http://ssnano.com/inc/sdetail/platinum_nanoparticles/8217?gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn4XH1pLOVQgRyj_fi_2SmvWo0k2nTc8JxmrJ_aoEWu8aArZ58P8HAQ| Seller]): '''192$/g''': in our case 780mg worth '''150$ | + | -200 nm sized nanparticles ([http://ssnano.com/inc/sdetail/platinum_nanoparticles/8217?gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn4XH1pLOVQgRyj_fi_2SmvWo0k2nTc8JxmrJ_aoEWu8aArZ58P8HAQ| Seller]): '''192$/g''': in our case 780mg worth '''150$'''. |
| − | -10 nm sized nanoparticles ([http://www.sciventions.com/product_info.php?cPath=19_44&products_id=126&gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn0uxkOwlip3945inSj1ZLbi2VU4ySIg4oG_pNODOMGgaAvqa8P8HAQ| Seller]) : '''2000$/g''' in our case, 780 mg worth '''1560$ | + | -10 nm sized nanoparticles ([http://www.sciventions.com/product_info.php?cPath=19_44&products_id=126&gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn0uxkOwlip3945inSj1ZLbi2VU4ySIg4oG_pNODOMGgaAvqa8P8HAQ| Seller]) : '''2000$/g''' in our case, 780 mg worth '''1560$'''. |
-50 nm sized nanoparticle purified coated with sodium citrate surface ([http://nanocomposix.eu/collections/platinum-nanoparticles/products/50-nm-platinum-nanoparticles| Seller]): roughly '''114,833$/g''': in our case 780mg worth approximately '''90,000$'''. | -50 nm sized nanoparticle purified coated with sodium citrate surface ([http://nanocomposix.eu/collections/platinum-nanoparticles/products/50-nm-platinum-nanoparticles| Seller]): roughly '''114,833$/g''': in our case 780mg worth approximately '''90,000$'''. | ||
Platinum utilization
The six Platinum Group Metals (i.e., platinum, palladium, rhodium, iridium, ruthenium and osmium) are chemically very similar and are used for many applications.
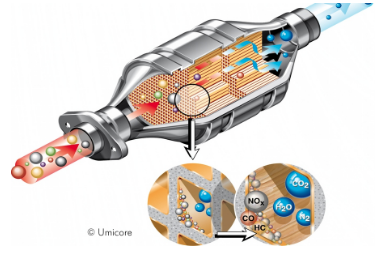
Autocatalyst
An autocatalyst is a cylinder or elliptical cross section made from ceramic or metal formed into a fine honeycomb and coated with a solution of chemicals and a combination of platinum, rhodium and/or palladium. It is mounted inside a stainless steel canister (the whole assembly is called a catalytic converter) and installed in a vehicle's exhaust line where it converts pollutants from the combustion of fuel into harmless gases. Without PGMs, the desired conversion reactions in the catalytic converter would not take place, resulting in the vehicle not meeting the emissions regulations. Other materials have been tried, but have not met the long term activity and durability requirements of modern-day emission control systems.
The amounts and proportions of PGM's depends on the age and type of vehicle :
- Cars, light-duty trucks, and motorcycles average total is 2-6 grams.
- Larger-engine SUV's and trucks average total can range anywhere from 6-30 grams.
The activity of the PGMs enables the reactions to occur at low temperature conditions that exist during cold starting of a vehicle, when emissions are at their highest. Durability is important since catalytic converters need to perform over the life of the vehicle. It also means that when an automobile is scrapped the precious metal contained in the catalytic converter is available for recycling, creating a valuable supplementary source to mining for the production of new autocatalysts. Platinum Group Metals are therefore an important features for the development of automobile industry.
Jewellery
Among the main advantages of platinum for jewellery fabrication are its strength and resistance to tarnish. In most of the countries in which platinum jewellery is manufactured, it is made in a purity of at least 85 per cent platinum. Other platinum group metals - palladium, ruthenium and iridium - and copper and cobalt are commonly alloyed with platinum to optimise its working characteristics and wear properties.
Electronics
Platinum and ruthenium are in computers and in the glass of computer screen. Without PGMs, there would be probably no computer, no mobile phone, no iGEM wiki... Each hard drive contains one or more platters or disks where data is stored on the magnetic surfaces. The strength of the magnetic field generated by the surface layer determines how much data can be recorded on a given surface. Adding platinum to the cobalt magnetic alloy enhances the magnetic properties of the surface and therefore its storage capacity.
Platinum, palladium, rhodium and iridium are used to coat electrodes, the tiny components in all electronic products which help to control the flow of electricity. Palladium is contained in most microprocessors and printed circuit boards. Platinum is used to make fiberglass, liquid-crystal display (LCD) glass and flat-panel displays, and cathode ray tubes. PGM equipment is used to make ceramic glass.
Medical
Platinum, for example, is used to create key components for a variety of medical devices, including pacemakers, catheters, stents, neuromodulation devices and implantable defibrillators. Platinum is also used in anticancer drugs such as cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin. It is the properties of this precious metal that makes it the material of choice for many medical applications: its biocompatibility, inertness with the human body, durability, electrical conductivity and radiopacity. In 2015, a review described the role played by platinum-based drugs in our society and all of the future applications that will rise through the new technology such as functional genomics. [1]
Nanoparticles
In all domains, nanoparticles are an emergent subject. Through their special abilities and properties, they will be a very powerful tool for future experiments Their main advantage is to have a very catalytic efficiency. As very tiny spheres the whole surface available for reaction are particularly large. In our process, we want to purify metals from plants or wastewater with siderophores, which are biological molecules naturally secreted by bacteria. Thanks to this process, we will create platinum nanoparticles, that are a high valuable form of this metal. That is why our process is relevant and look to the future! Platinum nanoparticles probably will be one of the most desired form of platinum in the next century...
Some platinum prices estimations have been made relying in available prices in websites. Let's consider the 780 mg produced in the final step are available at the end of the further purification steps :
-200 nm sized nanparticles ([http://ssnano.com/inc/sdetail/platinum_nanoparticles/8217?gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn4XH1pLOVQgRyj_fi_2SmvWo0k2nTc8JxmrJ_aoEWu8aArZ58P8HAQ| Seller]): 192$/g: in our case 780mg worth 150$.
-10 nm sized nanoparticles ([http://www.sciventions.com/product_info.php?cPath=19_44&products_id=126&gclid=Cj0KEQjwyJi_BRDLusby7_S7z-IBEiQAwCVvn0uxkOwlip3945inSj1ZLbi2VU4ySIg4oG_pNODOMGgaAvqa8P8HAQ| Seller]) : 2000$/g in our case, 780 mg worth 1560$.
-50 nm sized nanoparticle purified coated with sodium citrate surface ([http://nanocomposix.eu/collections/platinum-nanoparticles/products/50-nm-platinum-nanoparticles| Seller]): roughly 114,833$/g: in our case 780mg worth approximately 90,000$.
All our calculations are explained here.
- ↑ http://erc.endocrinology-journals.org/content/22/4/R219 Apps et al., 2015