Zigapusnik (Talk | contribs) |
Zigapusnik (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 180: | Line 180: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
<h4><span class="section"> </span>Abstract in plain English</h4> | <h4><span class="section"> </span>Abstract in plain English</h4> | ||
| − | <p>Synthetic biology aims to control cells so they can obey our commands and do what we want, for example to produce drugs when needed. In our project we made cells respond to ultrasound or touch. When we touch the cells they light up, which can be recorded on a camera. Ideally we want cells to respond to our commands as fast as possible, because sometimes we can’t wait an hour before the cells produce the medicine and release it. That is why we gave cells a novel mechanism of processing information. | + | <p> |
| + | <br /> | ||
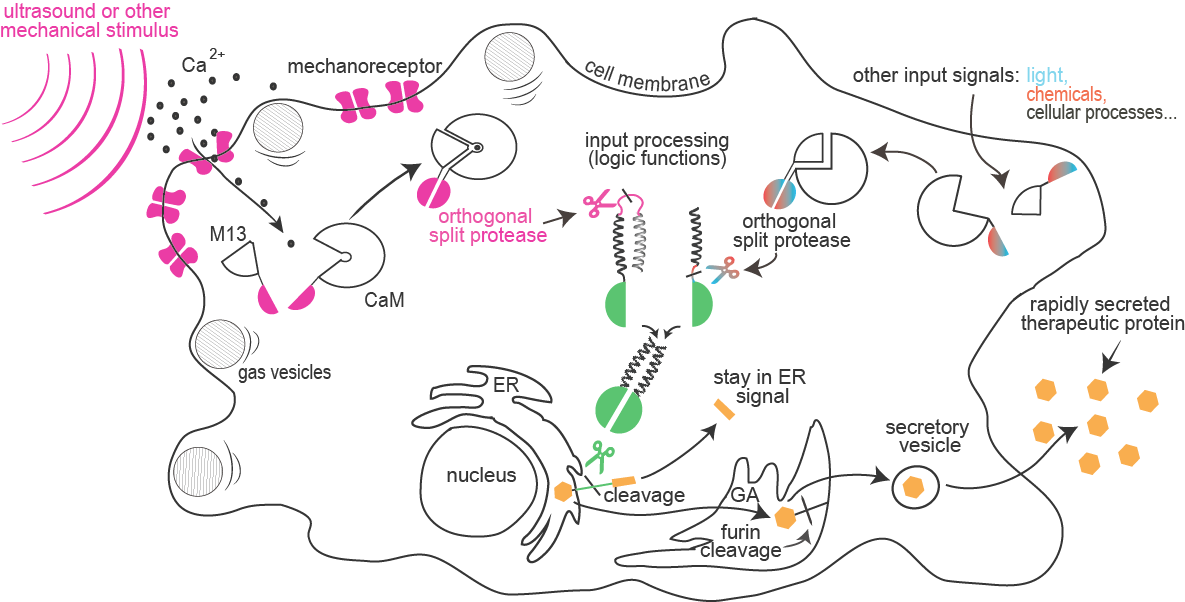
| + | Synthetic biology aims to control cells so they can obey our commands and do what we want, for example to produce drugs when needed. In our project we made cells respond to ultrasound or touch. When we touch the cells they light up, which can be recorded on a camera. Ideally we want cells to respond to our commands as fast as possible, because sometimes we can’t wait an hour before the cells produce the medicine and release it. That is why we gave cells a novel mechanism of processing information. | ||
We achieved this by combining several enzymes that recognize very specific parts of proteins and cut them, which changes their function. This allowed us to combine different signals, like sound, touch, light or chemicals, to obtain the desired cell response. The new enzymes can also cut the anchor with which medicines are attached to cells after the cells make them. Among many possible uses of our inventions, we can imagine activating cells in the brain by ultrasound, which means that we don’t need to use | We achieved this by combining several enzymes that recognize very specific parts of proteins and cut them, which changes their function. This allowed us to combine different signals, like sound, touch, light or chemicals, to obtain the desired cell response. The new enzymes can also cut the anchor with which medicines are attached to cells after the cells make them. Among many possible uses of our inventions, we can imagine activating cells in the brain by ultrasound, which means that we don’t need to use | ||
surgery to help people with Parkinson’s disease, or can trigger fast production of insulin in the body, to help people with diabetes. | surgery to help people with Parkinson’s disease, or can trigger fast production of insulin in the body, to help people with diabetes. | ||
Revision as of 11:08, 15 October 2016
Sonicell
Abstract in plain English
Synthetic biology aims to control cells so they can obey our commands and do what we want, for example to produce drugs when needed. In our project we made cells respond to ultrasound or touch. When we touch the cells they light up, which can be recorded on a camera. Ideally we want cells to respond to our commands as fast as possible, because sometimes we can’t wait an hour before the cells produce the medicine and release it. That is why we gave cells a novel mechanism of processing information.
We achieved this by combining several enzymes that recognize very specific parts of proteins and cut them, which changes their function. This allowed us to combine different signals, like sound, touch, light or chemicals, to obtain the desired cell response. The new enzymes can also cut the anchor with which medicines are attached to cells after the cells make them. Among many possible uses of our inventions, we can imagine activating cells in the brain by ultrasound, which means that we don’t need to use
surgery to help people with Parkinson’s disease, or can trigger fast production of insulin in the body, to help people with diabetes.
some other text
some other text
some other text
some other text



