Design
Source of platinum
Since a law from 1993, platinum is largely used in catalytic converter to avoid toxic gaz release [1]. . During the automobile fonctionnement, the precious metal is rejected and deposed on the road under a ionic form [2][3] Platinum leaching makes an accumulation of this metal on the road side. By default, it has been prooved that plants are potentiel bioaccumulator of platinum, which is found concentrated on the roots, leaves.. Otherwise, the metal is also carried on the sewage sludge and is actually an issue regarding the recycling potencial of these sludge
Mobilisation by a siderophore
In the previous article [4], authors made bioleaching with synthetised siderophores. By this way, they extracted approximately 80% of the total platinum found in the ore. But we were looking for a synthetic biological approach.
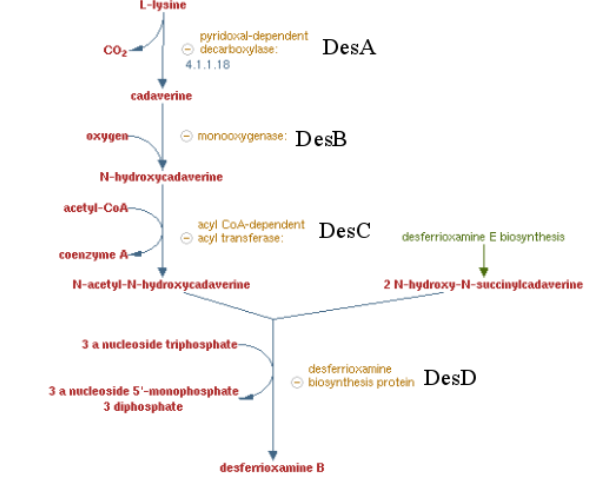
Pathway of the desferrioxamine B biosynthesis
Previous work showed that siderophore which are molecule secreted by bacteria to catch iron are able to catch other metals by default. Especifically, many articles showed a high affinity of Desferrioxamine B ( produce by Streptomyces coelicolor) for tetravalent metal ions and more specifically platinum. These results encouraged us to make a biobrick coding the sequence corresponding to the 4 enzymes involved on the metabolic pathway of Desferrioxamine B. E. coli was used to produce this biobrick. Produce a gram positive bacteria pathway in a gram negative bacteria is restrictive [5] , considering the risk of toxicity for the conductress bacteria. To counter this potential issue, we regulate trasnscription using the control of an inductible promotor (pBAD/araC).
Our strategy for the siderophore mobilisation results in two main steps :
1. Transformation of E.Coli with an inductible plasmide holding the des cluster
2. Induction and production of the desferrioxamine B
Then, the produced siderophore would be purified and transfered in the recuperation solution containing the platinum and other metals. Therefore, those metals must be recruit by our purified siderophores. Though those siderophores would be import using a sowing of Streptomyces coelicolor. Then simple centrifugation and combustion will concentrate the solution in metal a first time.
Biosorption and reduction using flagellin and peptides
This step aims to :
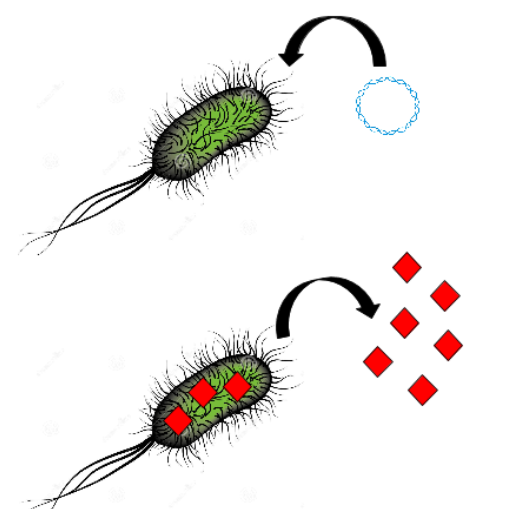
- adsorb ions on bacterial flagellar protein
- the ambient reducer power reduces ions into oxydised nanoparticules
- ↑ J. de Aberasturi, et al., Minerals Engineering 24, 505 (2011)
- ↑ P.S Hooda & al. 2007, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17604084
- ↑ Liliane Michel Legret & al. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11368-012-0491-3.
- ↑ Improving recoveries of platinum and palladium from oxidized Platinum-group element ores of the Great Dyke, Zimbabwe, using the biogenic siderophore Desferrioxamine B, Dennis Kraemer & al.
- ↑ Wandersman & Delepaire https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15487950
- ↑ Capeness & al. 2015, http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/27979/1/Michael%20Capeness%20-%20Thesis%20-%20PDF.pdf
- ↑ Deplanche & al., 2007 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/bit.21688/abstract. Furthermore, many peptides were generated based on sequences selected by phage display in order to enhance metal ions adsorpion including gold, silver and platinium.
All together, these findings incite us to use these natural properties to build a biobrick which is a high affinity binder of platinium based on E. coli and Desulfovibrio vulgaris flagellum and synthetic peptides sequences. To this end, we analyze the flagellin sequence and structural proprieties of the external part of the flagel. Then, on the part of the flagellin faced to the extarnal medium, an insertion restriction site will be inserted. Then specific precious metal peptides would be added using this insertion site to increase the level of adsorbsion specificity and yield. In this way, peptide would be faced to the external medium and able to bind metallic ions. To obtain a high transcription level of this sequence, we put transcription control under a strong promotor enabling a high flagellin production.
Next, the flagellin produced will be added to the first concentrated platinum solution. Flagellin containing specific peptides will bind the free or available ions of the medium and reduce them into oxydised nanoparticules usable in industry. A simple centrifugation of the flagellin binding to the platinum allow to concentrate the metal a second time.