Contents
Platinum utilization
The six Platinum Group Metals (i.e., platinum, palladium, rhodium, iridium, ruthenium and osmium) are chemically very similar and are used for many applications.
Autocatalyst
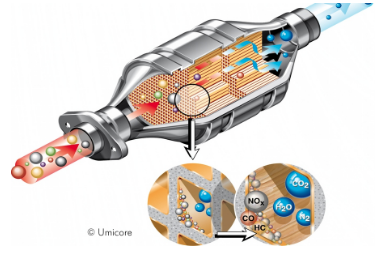
An autocatalyst is a cylinder or elliptical cross section made from ceramic or metal formed into a fine honeycomb and coated with a solution of chemicals and a combination of platinum, rhodium and/or palladium. It is mounted inside a stainless steel canister (the whole assembly is called a catalytic converter) and installed in a vehicle's exhaust line where it converts pollutants from the combustion of fuel into harmless gases. Without PGMs, the desired conversion reactions in the catalytic converter would not take place, resulting in the vehicle not meeting the emissions regulations. Other materials have been tried, but have not met the long term activity and durability requirements of modern-day emission control systems.The activity of the PGMs enables the reactions to occur at low temperature conditions that exist during cold starting of a vehicle, when emissions are at their highest. Durability is important since catalytic converters need to perform over the life of the vehicle. It also means that when an automobile is scrapped the precious metal contained in the catalytic converter is available for recycling, creating a valuable supplementary source to mining for the production of new autocatalysts. Platinum Group Metals are therefore an important features for the development of automobile industry.
Jewellery
Among the main advantages of platinum for jewellery fabrication are its strength and resistance to tarnish. In most of the countries in which platinum jewellery is manufactured, it is made in a purity of at least 85 per cent platinum. Other platinum group metals - palladium, ruthenium and iridium - and copper and cobalt are commonly alloyed with platinum to optimise its working characteristics and wear properties.Electronics
Platinum and ruthenium are in computers and in the glass of computer screen. Without PGMs, there would be probably no computer, no mobile phone, no wiki IGEM... Each hard drive contains one or more platters or disks where data is stored on the magnetic surfaces. The strength of the magnetic field generated by the surface layer determines how much data can be recorded on a given surface. Adding platinum to the cobalt magnetic alloy enhances the magnetic properties of the surface and therefore its storage capacity. Platinum, palladium, rhodium and iridium are used to coat electrodes, the tiny components in all electronic products which help to control the flow of electricity. Palladium is contained in most microprocessors and printed circuit boards. Platinum is used to make fiberglass, liquid-crystal display (LCD) glass and flat-panel displays, and cathode ray tubes. PGM equipment is used to make ceramic glass.