| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
color:orange; | color:orange; | ||
float:left; | float:left; | ||
| − | height: | + | height:80px; |
| − | line-height: | + | line-height:80px; |
vertical-align:middle; | vertical-align:middle; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
<div class="column full_size"> | <div class="column full_size"> | ||
<div class="divindiv" style="margin:auto"> | <div class="divindiv" style="margin:auto"> | ||
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/b/b4/T--Manchester--protocols_bigtitle.png" alt="symbol" style="width: | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/b/b4/T--Manchester--protocols_bigtitle.png" alt="symbol" style="width:120px;float:left;" /> |
<h1 class="sub_title">Medium and Buffers</h1> | <h1 class="sub_title">Medium and Buffers</h1> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 195: | Line 195: | ||
<li>Label the bottom of plates with antibiotic and date before storing in plastic bags or sealed with Parafilm at 4°C.</li> | <li>Label the bottom of plates with antibiotic and date before storing in plastic bags or sealed with Parafilm at 4°C.</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/5/52/T--Manchester--protocoltable5.png" alt="table 5" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Table source from <a href="https://www.neb.com/protocols/2012/06/21/making-your-own-electrocompetent-cells" target="_blank">New England Biolabs</a></p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><i>Additional note:</i></p> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Antibiotic carbenicillin can be substituted for ampicillin in antibiotic selection plates <sup>[1]</sup>.</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Source from <a href="https://www.addgene.org/plasmid-protocols/bacterial-plates/" target="_blank"></a></p> | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <button class="medium sub_sub_title">LB medium (Luria-Bertani medium)</button> | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 21:33, 23 September 2016


Medium and Buffers

- Prepare the solution by mixing the ingredients stated above.
- Sterilize in an autoclave before using it to prepare the SOC medium.

- Prepare the solution by mixing the ingredients stated above.
- Sterilize in an autoclave.
*Source from 2015 iGEM Exeter [link = 2015.igem2015 .org/wiki/images/a/ab/Exeter_Glycerol_recipe.pdf]
For nucleic acid DNA/RNA separation
- TAE buffer (Tris-acetate-EDTA)
- TBE buffer (Tris-borate-EDTA)
- LB buffer (Lithium borate)

- Prepare the solution by mixing the ingredients stated above.
If not using pre-mixed LB agar powder, prepare the materials as below:
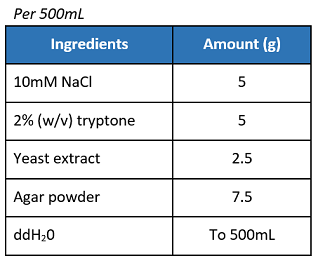
- In a 1L Erlenmeyer flask, swirl and mix the solution.
- Cover the top of the flask with a lid/aluminum foil and label with autoclave tape.
- Autoclave the liquid setting for 20 minutes or according to your autoclave's specifications.
- After removing the solution from the autoclave, allow the agar solution to cool to 55°C in an oven or water bath.
- When pouring the LB agar into plates, keep the bench area sterile by working near a flame or Bunsen burner. Alternatively, prepare the plates in a vacuum hood.
- Add the appropriate amount of desired antibiotic (refer the table below) to the solution and swirl to mix.
- Pour approximately 20mL of LB agar per 10cm polystyrene Petri dish.
- Place the lids on the plates and allow them to cool for until the agar is solidified.
- Label the bottom of plates with antibiotic and date before storing in plastic bags or sealed with Parafilm at 4°C.

Table source from New England Biolabs
Additional note:
- Antibiotic carbenicillin can be substituted for ampicillin in antibiotic selection plates [1].
















