| Line 478: | Line 478: | ||
<h3 style="color:#355E62;">A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 1</h3> | <h3 style="color:#355E62;">A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 1</h3> | ||
<h4>17 AUG | Blog Post 1</h4> | <h4>17 AUG | Blog Post 1</h4> | ||
| − | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Rachel Petherbridge, BostonU | + | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Rachel Petherbridge, BostonU</h4> |
| − | <h4> | + | <h4>An overview of the basics of intellectual property, which looks into background and definitions such as patent, copyright and trademark, as well as a roadmap to future posts.</h4> |
<h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/08/17/a-general-overview-of-intellectual-property-in-synthetic-biology-part-1/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | <h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/08/17/a-general-overview-of-intellectual-property-in-synthetic-biology-part-1/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 497: | Line 497: | ||
<h3 style="color:#355E62;">A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 2</h3> | <h3 style="color:#355E62;">A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 2</h3> | ||
<h4>22 AUG | Blog Post 2</h4> | <h4>22 AUG | Blog Post 2</h4> | ||
| − | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px"> | + | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW</h4> |
| − | <h4> | + | <h4>Further discussion of general intellectual property practices while drawing comparisons between intellectual property in synthetic biology and the software.</h4> |
<h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/08/22/a-general-overview-of-intellectual-property-in-synthetic-biology-part-2/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | <h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/08/22/a-general-overview-of-intellectual-property-in-synthetic-biology-part-2/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="col-md-2"></div> | <div class="col-md-2"></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 519: | Line 514: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row miniBio"> | <div class="row miniBio"> | ||
| − | <h3 style="color:#355E62;">A History of Intellectural Property, And Why it Matters to Synthetic Biology</h3> | + | <h3 style="color:#355E62;">A History of Intellectural Property, And Why it Matters to Synthetic Biology: Part 1</h3> |
<h4>11 SEPT | Blog Post 3</h4> | <h4>11 SEPT | Blog Post 3</h4> | ||
<h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW</h4> | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW</h4> | ||
| − | <h4>A | + | <h4>A brief history and discussion of the significance of intellectual property from the beginning of such laws in Venice in the late 1400s to the beginning of the copyright and patent system in the U.S. in the 1790s.</h4> |
<h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/09/11/a-history-of-intellectual-property-and-why-it-matters-to-synthetic-biology-part-1/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | <h4><a href="https://buigem2016.wordpress.com/2016/09/11/a-history-of-intellectual-property-and-why-it-matters-to-synthetic-biology-part-1/"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 532: | Line 527: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="row miniBio"> | <div class="row miniBio"> | ||
| − | <h3 style="color:#355E62;"> | + | <h3 style="color:#355E62;">A History of Intellectural Property, And Why it Matters to Synthetic Biology: Part 2</h3> |
| − | <h4> | + | <h4>19 OCT | Blog Post 4</h4> |
| − | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px"> | + | <h4><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/f/fa/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineAuthor_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW</h4> |
<h4>A short description of the article</h4> | <h4>A short description of the article</h4> | ||
<h4><a href="#"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | <h4><a href="#"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/0/00/T--BostonU_HW--blackOutlineBookmark_rcwolf.png" style="padding-right: 8px">Read more</a></h4> | ||
Revision as of 20:29, 18 October 2016
COLLABORATIONS
NEPTUNE Collaborative Findings
Given that Neptune was built to provide an accessible, affordable, and convenient solution for designing, manufacturing, and operating microfluidic systems, it was only natural that we would test our toolchain by designing microfluidics for other iGEM wetlab teams. We were able to collaborate with both the MIT iGEM team and the Northeastern iGEM team. Through these exchanges, we were able to test the Neptune workflow while providing a wetlab team with microfluidics to test their biological systems.
Building (Title of Chip)
SEPT - OCT 2016 | A collaboration with the MIT 2016 iGEM Wetlab Team
A description of our work with MIT

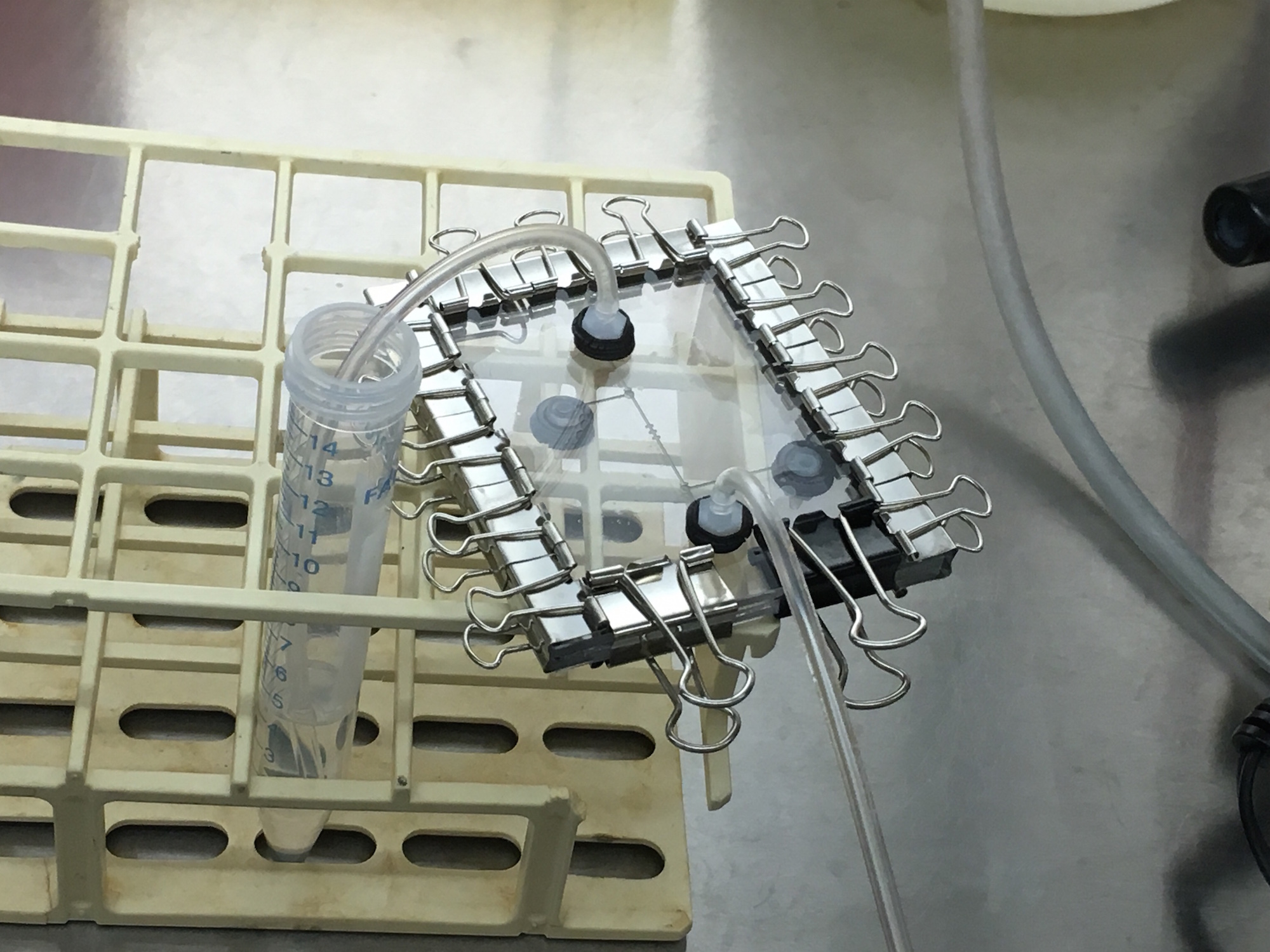


Designing a Cell Nutrient Starvation Inducer
AUG - SEPT 2016 | A collaboration with the Northeastern 2016 iGEM Wetlab Team
We designed a microfluidic device for Northeastern University's iGEM team to help characterize their starvation-induced genetic part, by flowing cells through a set of cell traps placed after a gradient generator, then flowing two variable amounts of nutrients through the inputs of the gradient generator, causing a variable amount of nutrients to hit each cell trap, and cause a variable expression level of the starvation-linked fluorescence. Unfortunately, due to difficulties on both sides, the device and the cells to put through it were never realized. The preliminary sketches and designs are shown here, however.

Open Source Materials and Synthetic Biology
Open source materials encourage a cooperative and connected community in any field of research. It allows individuals and labs to easily share their ideas for others to build off of and can inspire even greater creations. So we teamed up with the BU 2016 iGEM Wetlab Team to investigate the current place of open source materials in Synthetic biology and how, moving forward, open source materials could impact the direction of the field. We recorded our findings biweekly through posts in a collaborative blog entitled "Who Owns What".

A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 1
17 AUG | Blog Post 1
 Rachel Petherbridge, BostonU
Rachel Petherbridge, BostonU
An overview of the basics of intellectual property, which looks into background and definitions such as patent, copyright and trademark, as well as a roadmap to future posts.
 Read more
Read more

A General Overview of Intellectual Property in Synthetic Biology: PART 2
22 AUG | Blog Post 2
 Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW
Kestas Subacius, BostonU_HW
Further discussion of general intellectual property practices while drawing comparisons between intellectual property in synthetic biology and the software.
 Read more
Read more


