| Line 578: | Line 578: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | We examined whether farnesol also has an effect against food poisoning bacteria. | ||
[[File:阻止円実験.jpg|200px|thumb|center|State of the experiment:Effect of fregrance for growth of microbial]] | [[File:阻止円実験.jpg|200px|thumb|center|State of the experiment:Effect of fregrance for growth of microbial]] | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 16 October 2016
Result and Discussion
Confirmation antibacterial activity of farnesol.
First, we examined our working hypothesis to “Flavorator” that farnesol can show either the antibacterial or bacteriostatic activity in a box like “KOZOKO”. The results clearly showed that farnesol had antibacterial properties. In the literatures, farnesol have antibacterial volatiles. Farnesol is produced after complicated pathways, so for their syntheses, various enzymes are required. In E. coli, farnesol may be synthesized. In this context, we designed our system for establishing the concept of “Flavorator” to build up a brand-new biosynthetic pathways, in which farnesol is produced in the E. coli. In doing so, we transfered the three types of genes listed below to create the hyper-producer E. coli of farnesol. We examined our working hypothesis to “Flavorator” that farnesol can show either the antibacterial or bacteriostatic activity in a box like Kozoko.
Confirmation of anti-mold, anti-maggots and antibocatrial activities of farnesol.
E. coli can easily synthesize antimicrobial volatiles farnesol and geraniol. We examined the effects of three antimicrobial volatiles against bacteria which rot food.

A: geraniol(100 μl of geraniol solution was dropped on the cotton)B:farnesol(100 μl) C: ethanol (100 μl ) A:Chopstick dipped in suspension of mold was touched in the center of the bread. The volume of box is 846cm³. B:The same treatment was done. C:The same treatment was done. These boxes were kept for 5 days at room temperature.
Farnesol had the highest antifungal activity against mold.
We found that farnesol has high antifungal activity against the mold of bread. Therefore, we investigated whether farnesol exerts similar antifungal effects on other food.
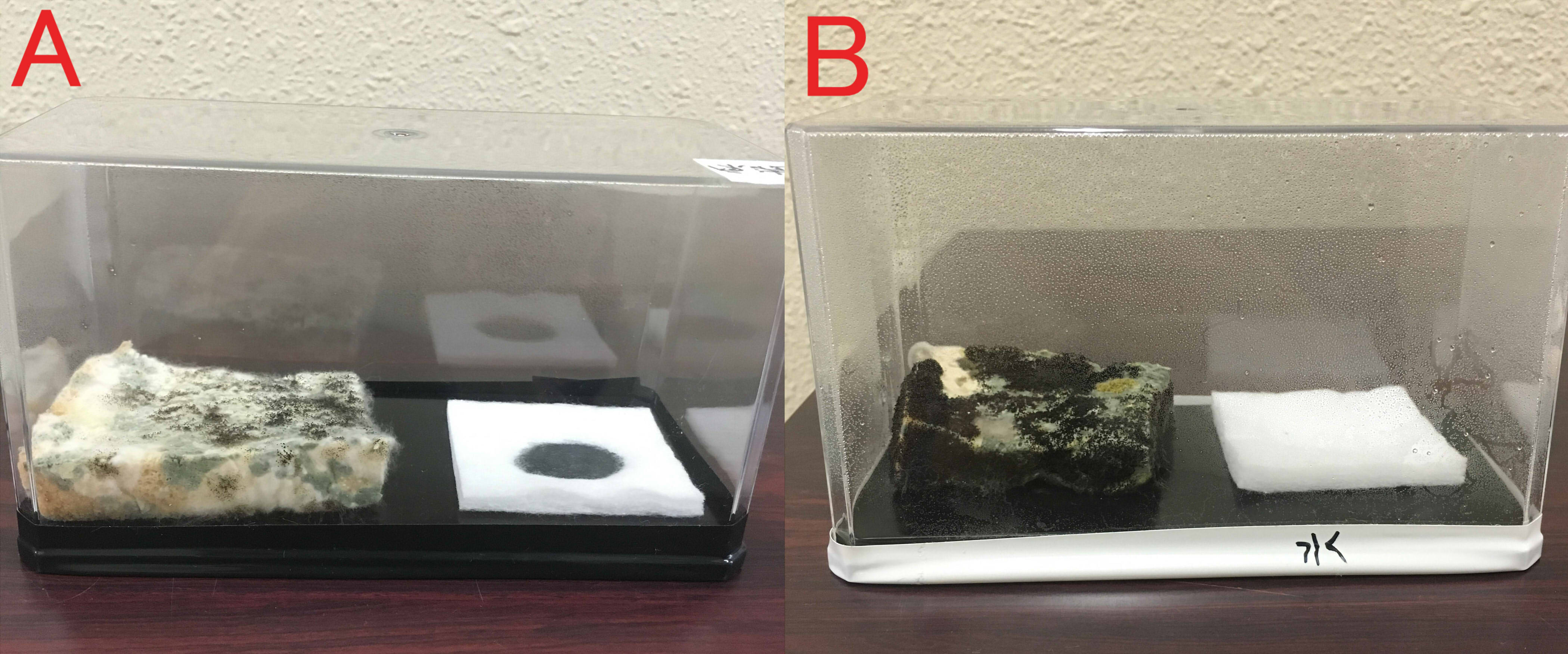

A: farnesol(1ml of farnesol solution was dropped on the cotton), B:ddH2O(1ml). A:Chopstick dipped in suspension of mold was touched in the center of the bread. The volume of box is 846cm³. B: The same treatment was done. These boxes were kept for 8 days at room temperature.
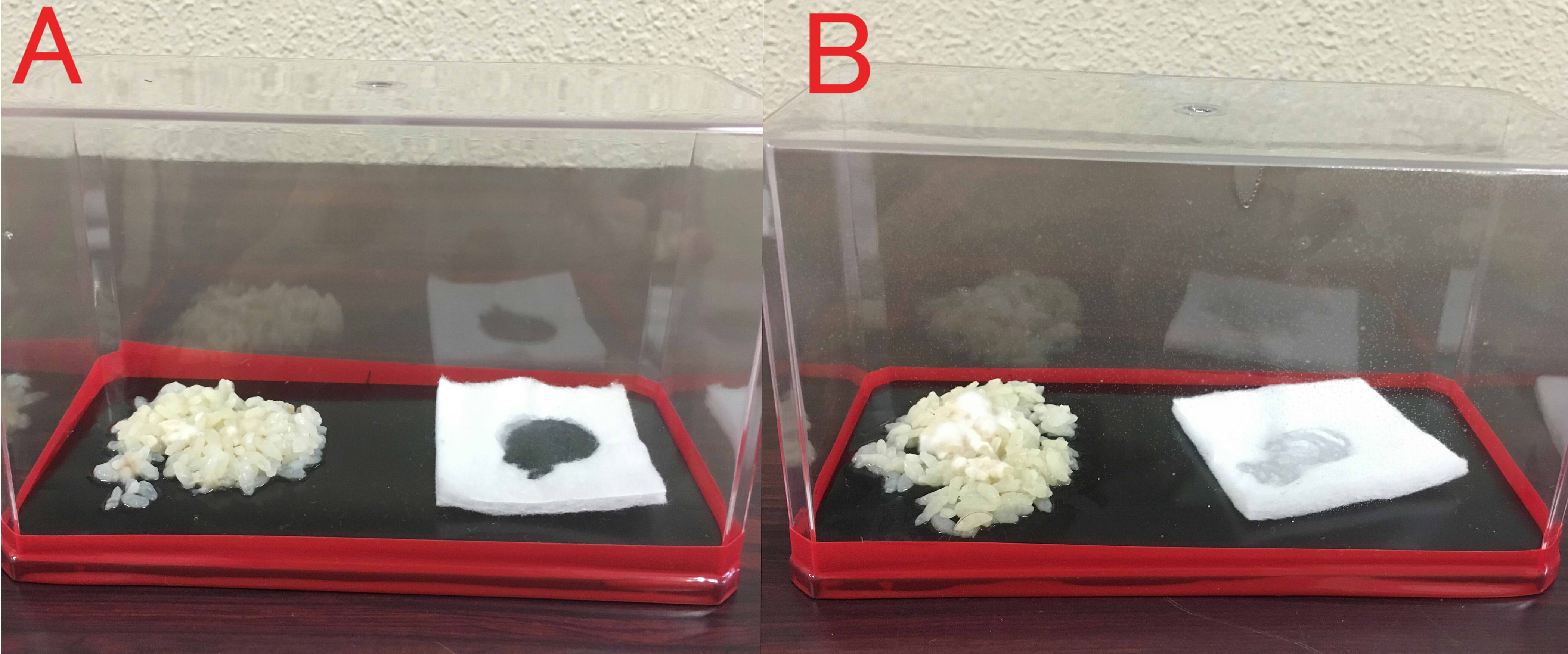

A: farnesol(1ml of farnesol solution was dropped on the cotton), B:ddH2O(1ml). A:Chopstick dipped in suspension of mold was touched in the center of the rice. The volume of box is 846cm³. B: The same treatment was done. These boxes were kept for 8 days at room temperature.

A: farnesol(1ml of farnesol solution was dropped on the cotton), B:ddH2O(1ml). A:Chopstick dipped in suspension of rotten meat was touched in the center of the chicken. The volume of box is 846cm³. B: The same treatment was done. These boxes were kept for 8 days at room temperature.
We found that farnesol has a preservative effect on various foods.
We examined whether farnesol also has an effect against food poisoning bacteria.