| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<h2>Introduction</h2> | <h2>Introduction</h2> | ||
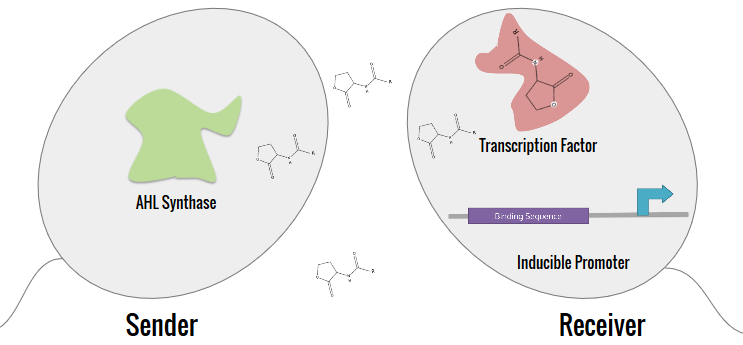
<p>The expanded characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) systems focused on 10 main systems, which are tabulated in the Project Description. The synthetic system that our team aimed to construct split the system into a Sender (AHL synthase) and a Receiver. By separating the inducer of the AHL from the receptor, crosstalk can be determined between systems. </p> | <p>The expanded characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) systems focused on 10 main systems, which are tabulated in the Project Description. The synthetic system that our team aimed to construct split the system into a Sender (AHL synthase) and a Receiver. By separating the inducer of the AHL from the receptor, crosstalk can be determined between systems. </p> | ||
| − | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/e/ed/T--Arizona_State--graphicoursystem.png"><br> | + | <center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/e/ed/T--Arizona_State--graphicoursystem.png"></center><br> |
<h2>Bacterial Cloning</h2> | <h2>Bacterial Cloning</h2> | ||
<p>E. coli DH5αT was used for the construction of the Senders and Receivers. BL21(DE3) E. coli was used for induction tests. After long transformation, liquid cultures were made using LB broth mixed with ampicillin. All cultures were then appropriately digested and ligated in order to properly construct each part. A modular receiver and modular sender vectors were developed for each of the parts. The designs for these plasmids are shown below. </p> | <p>E. coli DH5αT was used for the construction of the Senders and Receivers. BL21(DE3) E. coli was used for induction tests. After long transformation, liquid cultures were made using LB broth mixed with ampicillin. All cultures were then appropriately digested and ligated in order to properly construct each part. A modular receiver and modular sender vectors were developed for each of the parts. The designs for these plasmids are shown below. </p> | ||
Revision as of 08:27, 12 October 2016
Results
Introduction
The expanded characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) systems focused on 10 main systems, which are tabulated in the Project Description. The synthetic system that our team aimed to construct split the system into a Sender (AHL synthase) and a Receiver. By separating the inducer of the AHL from the receptor, crosstalk can be determined between systems.
Bacterial Cloning
E. coli DH5αT was used for the construction of the Senders and Receivers. BL21(DE3) E. coli was used for induction tests. After long transformation, liquid cultures were made using LB broth mixed with ampicillin. All cultures were then appropriately digested and ligated in order to properly construct each part. A modular receiver and modular sender vectors were developed for each of the parts. The designs for these plasmids are shown below.


Here you can describe the results of your project and your future plans.
What should this page contain?
- Clearly and objectively describe the results of your work.
- Future plans for the project
- Considerations for replicating the experiments
Project Achievements
You can also include a list of bullet points (and links) of the successes and failures you have had over your summer. It is a quick reference page for the judges to see what you achieved during your summer.
- A list of linked bullet points of the successful results during your project
- A list of linked bullet points of the unsuccessful results during your project. This is about being scientifically honest. If you worked on an area for a long time with no success, tell us so we know where you put your effort.
Inspiration
See how other teams presented their results.

