| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
<p>After having the essential kombucha microbes, the next set of recapitulations tested what ratios these microbes needed to be in when placed in tea media so they could properly form a SCOBY and recreate kombucha. This process involved multiple trial and error results, but eventually the results included below were found. | <p>After having the essential kombucha microbes, the next set of recapitulations tested what ratios these microbes needed to be in when placed in tea media so they could properly form a SCOBY and recreate kombucha. This process involved multiple trial and error results, but eventually the results included below were found. | ||
| + | <center> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/38/T--Austin_UTexas--PreviousRecaps.png" style="width:500px;display:inline-block"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/3/38/T--Austin_UTexas--PreviousRecaps.png" style="width:500px;display:inline-block"> | ||
| Line 233: | Line 234: | ||
<figcaption><b>Figure 2:</b> Shows samples from a series of completed recapitulation trials. A negative control triplicate set contained only tea media and experienced no microbial growth after 7 days. The positive control was inoculated with 600 uL of home-brewed kombucha and possessed distinct pellicle formation after 4 days, forming a mature pellicle by Day 7. Both experimental trials pictured yielded successful recapitulations. Row 3 shows a set of trials that incorporated both microbes that had been purchased and microbe that had been isolated from kombucha itself. Row 3 shows successful recapitulations that contained two different strains of <i>Lachancea fermentati</i> each isolated from kombucha samples, as well as a strain of and <i>Gluconacetobacter hansenii</i>. The cellulose pellicle produced in this set of trials is thick and has multiple carbon dioxide bubbles.</figcaption> | <figcaption><b>Figure 2:</b> Shows samples from a series of completed recapitulation trials. A negative control triplicate set contained only tea media and experienced no microbial growth after 7 days. The positive control was inoculated with 600 uL of home-brewed kombucha and possessed distinct pellicle formation after 4 days, forming a mature pellicle by Day 7. Both experimental trials pictured yielded successful recapitulations. Row 3 shows a set of trials that incorporated both microbes that had been purchased and microbe that had been isolated from kombucha itself. Row 3 shows successful recapitulations that contained two different strains of <i>Lachancea fermentati</i> each isolated from kombucha samples, as well as a strain of and <i>Gluconacetobacter hansenii</i>. The cellulose pellicle produced in this set of trials is thick and has multiple carbon dioxide bubbles.</figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| − | + | </center> | |
| − | + | ||
<center><a href="#top"><p>Back to Top</p></a></center> | <center><a href="#top"><p>Back to Top</p></a></center> | ||
Revision as of 21:22, 19 October 2016
Results

Click on one of the images below to learn more about our results!
Kombucha Strains
The first steps in the characterization of microbes native to kombucha involved the isolation of strains from store-bought kombucha samples. This was accomplished by plating various dilutions of kombucha onto a variety of media including YPD, HS, and R2A.

Isolated colonies were selected from each "isolation plate" and continually grown up and streaked out to ensure that the resulting frozen stock was truly axenic. Each newly isolated microbe was designated with a "KOM #" based on the order in which it was isolated (i.e. KOM 01, KOM 02, etc.) to serve as a placeholder name until the species could be identified. In order to begin this identification process, genomic DNA (gDNA) was first isolated from each individual strain. This DNA was then used as the template for two separate PCR reactions targeting either the 16S rRNA gene in bacteria, or the ITS rRNA gene for fungi. PCR products were then run on a 1% agarose gel to observe which reaction yielded product in gel.
Once it was determined whether each isolate was a bacterium or a fungus, the PCR products were purified and samples of the gDNA was sequenced using Sanger sequencing. The resulting sequences were then run through the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) SeqMatch tool in order to identify the exact species of bacteria or yeast that correspond to each tested isolate. The identified microbes are listed below in Table 1.

| Species | Classification | Brand of Kombucha Isolated From |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus warneri | Bacteria | GT’s Kombucha |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Bacteria | GT's Kombucha |
| Gluconobacter oxydans* | Bacteria | GT’s Kombucha |
| Lachancea fermentati* | Yeast | Buddha's Brew |
| Propionibacterium acnes | Bacteria | Buddha's Brew |
| Micrococcus luteus | Bacteria | Buddha's Brew |
| Bacillus pumilus | Bacteria | Buddha's Brew |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Yeast | LIVE Soda Kombucha |
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe* | Yeast | LIVE Soda Kombucha |
(*Indicates a species that is considered vital to the production of kombucha)
Back to Top
Conjugation
We have attempted to conjugate GFP into both G. oxydans and G. hansenii with a Diaminopimelic Acid (DAP) auxotrophic strain of E. coli (The Barrick Lab). The plasmid contains the vector pMMB67EH, the promoter PA-1, GFP and a spectinomycin resistance gene.
The first conjugation was done with two of our isolated G. oxydans strains, in case the strains might behave differently. First, a mixture between our recipient strain and the DAP auxotroph strain were plated on an LB+DAP agar plate to allow for conjugation to occur. After 24 hours of incubation, we scraped up the growth and plated each conjugation mixture onto a LB+Spec plate. 24-48 hours later, we viewed the potential transconjugants using a fluorescence microscope. We then picked these glowing colonies and streaked them out onto another LB+Spec plate. We then followed our protocol for genome DNA isolation and 16S sequencing, as described above, to confirm successful conjugation of G. oxydans. After troubleshooting our 16s procedure, we were finally able to obtain a viable sequencing result. However, all of the glowing colonies were identified as E. coli.

For the next round of conjugation, we used a strain of both G. oxydans and Gluconacetobacter hansenii from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Our procedure was identical to the one described in the previously paragraph.
We then picked isolated colonies and streaked them out onto LB+Spec plates. After using 16s sequencing on the potential transconjugants, we encountered an anomaly. Instead of amplifying the 16s gene, we received the sequence of the L,D Transpeptidase gene of E. coli.
We then decided to perform a Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) experiment in order to determine if G. oxydans is able to survive antibiotics above the standard E. coli concentration. We tested the antibiotics kanamycin, spectinomycin and carbenicillin.
Our results showed that G. oxydans is resistant to at least 4x concentrations of spectinomycin (1x = 60µg/mL) and carbenicillin (1x = 100µg/mL). However, a 1x concentration of kanamycin (1x = 50µg/mL) was sufficient to inhibit growth. With this information, we then performed conjugations with E. coli donors that had a kanamycin resistance. These results are still pending through the wiki freeze.

Back to Top
Recapitulation
The process of recapitulations took individual microbes, isolated from kombucha, and recombined these to reform kombucha. This process is essential to create a designer beverage: the microbes that have been taken from kombucha and genetically engineered must be able to be put back together to remake kombucha. The process of recapitulation was repeated multiple times in triplicate. Each trial tested a different growing condition or different combinations of microbes for regenerating kombucha.
The first trials of recapitulations tested the tea media being used to compare the tea that at-home brewers used to see if this would support the microbial growth of isolates. The next trials performed used strictly the microbes isolated from kombucha, the problem with this approach is that not all microbes that occur in kombucha can be isolated away from the symbiotic they exist in, and further they cannot grow on a solid agar plate. Using the previous research on kombucha found in scientific literature, as well as our findings in lab, the most prominent microbes that help to create kombucha were attained (either by isolation from kombucha or by purchasing from a scientific database) to be used in future recapitulations.
After having the essential kombucha microbes, the next set of recapitulations tested what ratios these microbes needed to be in when placed in tea media so they could properly form a SCOBY and recreate kombucha. This process involved multiple trial and error results, but eventually the results included below were found.


Back to Top
Ethanol Reduction



Approach
Two potential ways to reduce ethanol content over the course of the fermentation are to reduce the rate at which yeast produce ethanol or increase the rate at which acetic acid bacteria convert the ethanol to acetic acid. The first of these methods is the most direct approach, and was the first method considered. We considered UV mutagenizing Lachancea fermentati, a yeast our lab has isolated from kombucha, and then screening for ethanol production using a pH indicator, bromothymol blue, in media (Figure 1). Bromothymol blue is blue at basic pH, turns green around pH 7, and turns yellow around pH 6, and has been used previously to screen for fermentation rate among Saccharomyces cerevisiae colonies (Robillard, 2007). During anaerobic respiration, both ethanol and CO2 are produced, and CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid, lowering the pH of the plate and changing the color of the indicator. A variety of problems with this approach led us to abandon it. It is likely that L. fermentati produce other acidic metabolic products, so pH would not necessarily correspond to amount of ethanol produced. This assay also relies on distinguishing differences in color in the agar to tell the difference in ethanol production between two colonies, a process that would be somewhat subjective. Additionally, the ethanol produced is necessary for the production of acetic acid, so slowing the rate of ethanol production would likely have slowed the production of the beverage and could have thrown off the flavor. For all these reasons, attempting to decrease the rate of ethanol production by L. fermentati does not seem like a good approach to lowering the ethanol content during the fermentation.
We next considered increasing the rate at which acetic acid bacteria in kombucha convert ethanol to acetic acid. Increasing this rate would utilize more ethanol as it is produced, ideally lowering the ethanol content throughout the course of the fermentation. Two enzymes facilitate steps in this pathway (Mamlouk and Gullo, 2013). An alcohol dehydrogenase (PQQ-ADH) enzyme facilitates the conversion of ethanol to acetaldehyde, and a membrane-bound aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) facilitates the conversion of acetaldehyde to acetic acid. In order to increase the rate at which ethanol is converted into acetic acid, we propose using Golden Gate Assembly to create a genetic construct in which expression of PQQ-ADH and ALDH is governed by a Tac-promoter (pTac), a hybrid promoter which is inhibited except in the presence of allolactose. The construct would be transformed into electrocompetent Escherichia coli and transferred to Gluconacetobacter hansenii via conjugation.
Identifying genes of interest
In order to design a construct increasing expression of PQQ-ADH and ALDH in Ga. hansenii, it was necessary to find the genome of the ATCC strain and identify the coding sequences for these genes. The whole genome shotgun sequence for our organism, ATCC 53582, is published on NCBI (Abbot, 2015) with annotations regarding the functions of specific sequences. Coding sequences are annotated with proposed gene products. Though there are several aldehyde dehydrogenase genes annotated in the genome, there is only one which is described as membrane-bound, matching the description from Mamlouk and Gullo (Mamlouk and Gullo, 2013). There are additionally multiple alcohol dehydrogenases. A known amino acid sequence for a homologous PQQ-ADH in Comamonas testosteroni was compared against sequences in the Ga. hansenii genome using BLAST (Table 1). One ADH enzyme found in the Ga. hansenii genome sequence matches the C. testosteroni sequence with a query cover value of 94% and an E value of 0 (third line of Table 1).
Creation of Golden Gate parts
In order to assemble the construct, the coding sequences for the genes of interest must be amplified from the Ga. hansenii genome and edited such that they have the correct Golden Gate overhangs and no internal BsaI or BsmBI restriction sites. The sequences were uploaded to Benchling for analysis and planning. The coding sequence for the membrane-bound ALDH contains a BsaI restriction site near the middle of the gene (Figure 2), and the PQQ-ADH coding sequence contains a BsmBI restriction site near the end of the gene (Figure 3). To eliminate the BsaI site in ALDH, primers were designed that would introduce a point mutation at the restriction site. One set of primers, igem2016_KOM_EtOH_01 and igem2016_KOM_EtOH_02, amplifies the sequence upstream of the restriction site, adding a type 3 Golden Gate prefix and removing the restriction site. Another set, igem2016_KOM_EtOH_03 and igem2016_KOM_EtOH_04, amplifies the region downstream of the restriction site, introducing a mutation to the site and adding a type 3 Golden Gate suffix to the end of the gene. These two products will be used in an overlap PCR reaction to create a final product with no BsaI restriction sites and the correct prefix and suffix for assembly. To remove the BsmBI site from the PQQ-ADH coding sequence, a set of primers (igem2016_KOM_EtOH_05 and igem2016_KOM_EtOH_06) was designed to amplify the region upstream of the restriction site and add a Golden Gate type 3 prefix to the beginning of the sequence. The reverse primer additionally adds a mutation to existing BsmBI restriction site and creates a new BsmBI restriction site that will be used to join the piece to a double-stranded DNA, igem2016_KOM_EtOH_07, containing the rest of the gene’s coding sequence appended with a Golden Gate type 3 suffix. The assembly of the PQQ-ADH part will therefore take place in two reactions: one reaction in which the upstream piece of DNA is created, and one reaction in which it is ligated to the gBlock. Table 2 contains more information about each of these oligonucleotides. All were ordered from IDT.
Back to Top
pH Sensors
During the kombucha brewing process, the beverage becomes more acidic. Additionally, it is unclear if or how the microbial community changes within the beverage over time. Thus, our team decided to find pH sensitive promoters that could be used to track not only the pH of the maturing beverage, but also the presence of the various microbes within the kombucha over time. We successfully created a neutral range reporter, attempted to create acidic and basic range reporters, and found three putative acidic range reporters that are endogenous to one of our kombucha bacteria, Gluconobacter oxydans
Though an acidic sensor was what was required for our kombucha analysis, the identification of sensors in other areas of the pH spectrum were explored as well. Three sequences were identified, the CadC operon for the acidic range, CpxA-CpxR complex for the neutral range, and the P-atp2 promoter from the BioBrick Registry (BBa_K1675021) for the basic range. Each sequence was paired with a unique corresponding reporter sequence so that if each pH sensitive plasmid were in the same environment, the specific pH of the system could be seen. The reporters used were, BBa_E1010 for the CadC construct, BBa_K1033916 for the CpxA-CpxR complex, and BBa_K592009 for the P-atp2 promoter.
CpxA-CpxR

CpxA-CpxR is a two-component mechanism that is activated at pH 7.4 and repressed at pH 6.0. CpxA is an intermembrane protein that autophosphorylates at a certain external pH, CpxR (a kinase) then gets phosphorylated by CpxA and acts as a transcription factor. This system originally is a transcription factor for the virF gene, but virF was replaced with a reporter. The original sequence was found in Shigella sonnei, but E. coli has a homolog of these proteins so all that is required on the construct is the appropriate prefix/suffix and CpxR binding site (Nakayama and Watanabe, 1995; Nakayama and Watanabe, 1998).
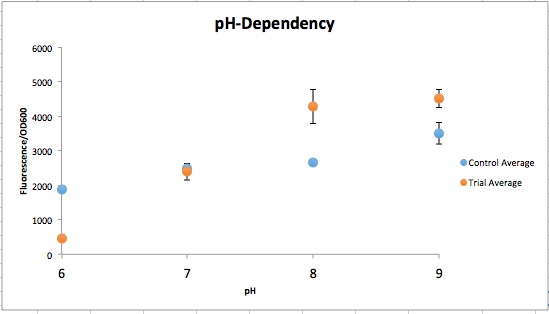
The order from left to right in figure 1 is control pH 6-9 and then Experimental pH 6-9. These are showing the gradient change in expression accordingly with the change of pH due to a pH-dependent promotor compared to consistent expression accordingly with a promoter that is always "on". The main point is that the control at pH 6 has more expression of the yellow-green chromoprotein than the Experimental at pH 6. The pH-dependent promoter of the experimental group is down-regulated at pH 6 whereas the control is not. Also, there is an increase in YGCP expression between the experiment pH 7 and pH 8 that is not seen in the control between pH 7 and pH 8. The normalized data in figure 2 shows the relative expression of YGCP. The CpxA-CpxR construct can be found on the iGEM registry as: BBa_K2097000, while the construct utilized as a control can be found on the iGEM registry as BBa_K2097002 as well as in figure 3.
CadC
The CadC operon is a native pathway in E. coli, involved in the cadaverine synthesis pathway. The protein CadC protein on the operon is produced and activates segments downstream of the operon on the CadBA receptors. The CadC protein is pH sensitive to an external pH 5.5 and below, as well as lysine dependent. A point mutation on codon 265, in which argenine is converted to cystine, causes the CadC protein to become lysine independent (Kuper and Jung, 2005).
Despite several attempts, we have been unable to grow the modified CadC operon on pSB1C3 in E. coli suggesting some form of cell toxicity. Specifically, all plasmids isolated have contained additional point mutations that appear to inactivate the expression of CadC. Due to this apparent toxicity, no data regarding the lysine-independent CadC could be collected. Alternative acidic range pH sensor candidates have been identified and are discussed below.
P-atp2
The P-atp2 promoter, native to the bacterium Corynebacterium glutamicum is reportedly induced at pH 7, to pH 9 (BIT-China-2015 and BBa_K1675021). Utilizing the blue chromoprotein (BBa_K592009), a test was designed in which a plasmid containing the P-atp2 promoter with the blue chromoprotein was grown alongside an E. coli line that contained a plasmid with just the blue chromoprotein. We expected to see constant blue chromoprotein production in the control series (those that lacked P-atp2) and a visual increase in blue chromoprotein as the pH was raised from 6 to 9 in the cells that contained the P-atp2 construct. The construct utilized as a control can be found on the iGEM registry BBa_K2097001 as as in figure 5.
However, as seen in figure 4, no clear change in color expression appears in the experimental trials, suggesting a lack of sensitivity of the P-atp2 promoter.
GOX Sequences as Putative Promoters
Three endogenous upstream regions of loci on the Gluconobacter oxydans chromosome were reported to show increased mRNA synthesis as pH decreased, were isolated and obtained, as seen in table 1 (Hanke, et al., 2012). Using Golden Gate assembly, these putative promoters have been placed on the Golden Gate entry vector pYTK001 for later use. By utilizing these pH-sensitive promoters with different reporters and transforming them into multiple organisms in kombucha, the visualization of the microbes and their location in kombucha would be possible (Lee, et al., 2015). This will serve as a stepping stone into further understanding how the microbiome of kombucha changes as it brews as well as determining organism concentration specific times during the brewing process.
| Locus Tag | Predicted Functions | mRNA ratio pH4/pH6 |
|---|---|---|
| GOX0647 | Putative exporter protein, ArAE family | 12.91 |
| GOX0890 | Hypothetical protein GOX0890 | 4.93 |
| GOX1841 | Hypothetical protein GOX1841 | 3.36 |
Gellan Gum

The do-it-yourself (DIY) movement is focused on making science more accessible to the public. Because many consumers brew their own kombucha, we have developed a set of DIY instructions that would allow an average person to analyze their home-brew and identify their kombucha’s species outside of a lab setting. This procedure is possible because of Gellan Gum, produced by the halobacterium Sphingomonas pauci-mobilis.
Gellan Gum is produced through aerobic fermentation (Kang et al. 1982). This exopolysaccharide is a “high-molecular-mass, anionic polysaccharide which consists of a tetrasaccharide structure with 20% glucuronic acid, 60%glucose, and 20% rhamnose” (Wang et. al. 2006). The advantages of using Gellan in place of agar include: requiring half of the quantity, a consistent production, more clarity than agar, a reduced plate preparation time along with a faster setting time, stability at high temperatures, and lack of contamination factors found in agar that are toxic to some organisms (Ioannis et. al. 2007).
This protocol involves creating media from every-day grocery store items, autoclaving or microwaving a culture of S. paucimobilis for sterilization, then pouring them into plates which can be streaked with microbes. Figure 1 denotes each of the steps of the protocol. An S. paucimobilis colony is initially grown in conditions that focus the cell’s metabolism on multiplication. This maximizes the number of cells producing Gellan when inoculated into minimal media (Wu et. al. 2014).
We tested this protocol by growing Escherichia coli on LB-Gellan plates and by growing Saccharomyces cerevisiae on YPD-Gellan plates. Both microbes successfully grew on Gellan plates as in Figure 2 and Figure 3. We then confirmed the viability of Gellan-tea media plates to be used for kombucha by streaking various strains that we isolated from Kombucha.
In addition to being usable in this DIY procedure, Gellan Gum is environmentally and socially conscious. Currently there is an agar shortage in the world, because of several threats to its origin, red algae (Calloway 2015).
References
- The Barrick Lab Conjugation Protocol
- Abbot, J. Komagataeibacter xylinus isolate ATCC53582 genome assembly, contig: ATCC53582_Chromosome, whole genome shotgun sequence. 2015. Accessed from NCBI website.
- BIT-China-2015
- Calloway, Ewen. (2015) Lab staple agar hit by seaweed shortage. Nature.
- Hanke, T., Richhardt, J., Polen, T., Sahm, H., Bringer, S., and Bott, M. (2012) Influence of oxygen limitation, absence of the cytochrome bc1 complex and low pH on global gene expression in Gluconobacter oxydans 621H using DNA microarray technology. Journal of Biotechnology 157, 359–372.
- Ioannis Giavasis et al. (2000) Gellan Gum Critical Reviews in Biotechnology., 20.3: 177-211
- Kang, Kenneth S. et al. (1982) Agar-Like Polysaccharide Produced by a Pseudomonas Species: Production and Basic Properties. Applied and Environmental Microbiology., 1086-1091
- Kuper, C., and Jung, K. (2005) CadC-mediated activation of the cadBA promoter in Escherichia coli. Journal of Molecular and Microbiological Biotechnology 1, 26–39.
- Lee ME, DeLoache, WC A, Cervantes B, Dueber, JE. (2015) A Highly-characterized Yeast Toolkit for Modular, Multi-part Assembly. ACS Synthetic Biology 4 975-986
- Mamlouk, Y. and M. Gullo. Acetic Acid Bacteria: Physiology and carbon sources oxidation. 2013. Indian Journal of Microbiology 53 (4): 337-384.
- Nakayama, S.-I., and Watanabe, H. (1998) Identification of cpxR as a Positive Regulator Essential for Expression of the Shigella sonnei virF Gene. Journal of Bacteriology 180, 3522–3528.
- Nakayama, S.-I., and Watanabe, H. (1995) Involvement of cpxA, a Sensor of a Two-Component Regulatory System, in the pH-Dependent Regulation of Expression of Shigella sonnei virF Gene. Journal of Bacteriology 177, 5062–5069.
- Robillard, R. A microbial breathalyzer: design of a colorimetric assay for the detection and quantification of ethanol production in microbes. 2007. Major qualifying project for a B.S. degree from Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
- Wang, Xia, et al. (2006) Modeling for Gellan Gum Production by Sphingomonas paucimobilis ATCC 31461 in a Simplified Medium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 3367-3374
- Wu et. al. (2014) Yellow pigments generation deficient Sphingomonas strain and application thereof in Gellan Gum. US Patent 8,685,698.
Back to Top