RFC10 Standard Yeast Vectors
pSB416-GPD:RFC 10 Compatibile URA3-selectable S. cerevisiae Expression Vector
Overview
This is a RFC10 standard yeast expression vector adapted from the widely used plasmid p416-GPD. The MCS of p416-GPD was replaced with the standard BioBrick prefix and suffix and an illegal PstI restriction site near the URA3 promoter of p416-GPD was removed. In the resultant plasmid, pSB416-GPD (5743 bp), the BioBrick prefix and suffix is situated between the yeast GPD promoter and CYC1 terminator allowing for facile cloning and expression of translational units in yeast. M13 primers flank the transcriptional unit. The plasmid has a ColE1 origin and ampicillin resistance for replication in E.coli. It also contains a yeast CEN/ARS providing high fidelity maintenance and low copy number in yeast. We used this vector to express mRPS12 TU and mls-yeGFP in BY4741 S. cerevisiae.
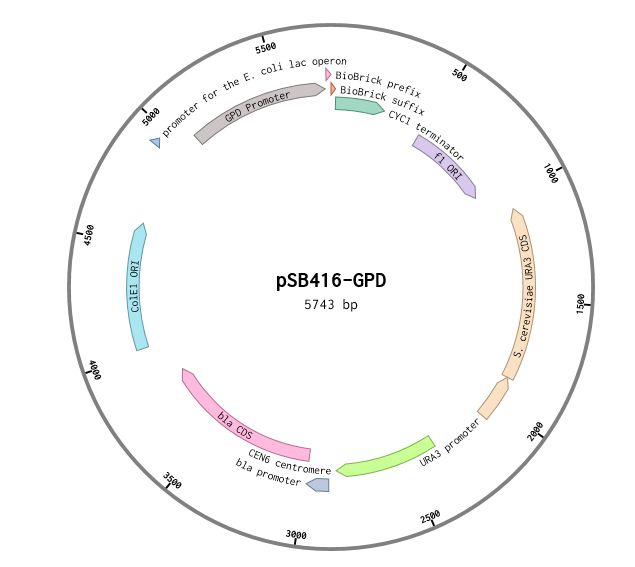
Design
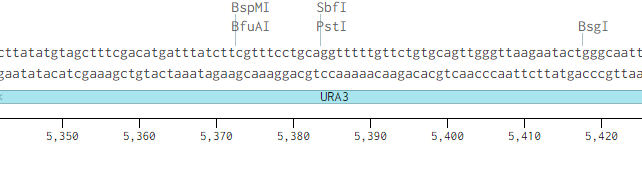
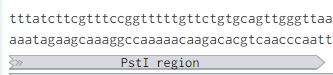
Originally p416-GPD had an illegal PstI site in the URA3 promoter region.
Removing the PstI site from p416 GPD required simply cutting with SbfI, blunting the sticky ends of the DNA removing the PstI site, and then ligating the plasmid back together. Giving us the resulting region with the PstI site removed.
We also needed to replace the MCS in pSB416-GPD with the RFC 10 standard prefix and suffix. We removed the MCS in p416-GPD by cutting the XbaI and XhoI removing the MSC from the p416-GPD plasmid.
pSB413-GPD: RFC 10 HIS3-selectable S. cerevisiae Expression Vector
Overview
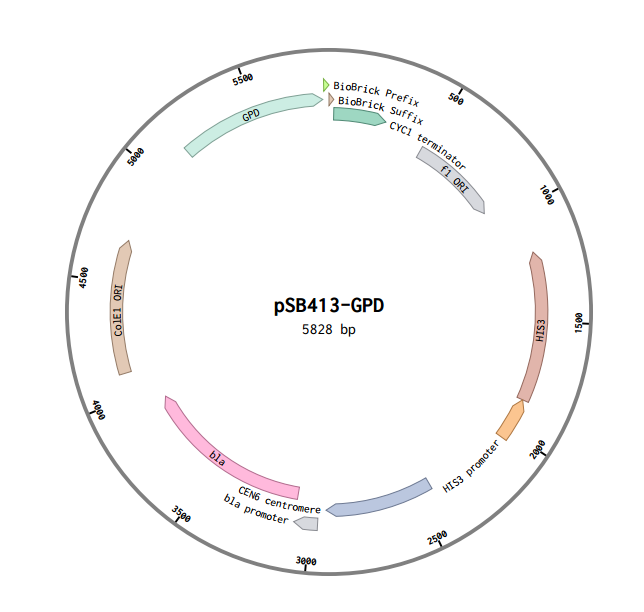
This is a RFC10 standard yeast expression vector adapted from the widely used plasmid pSB413-GPD. The MCS of p413-GPD was replaced with the standard BioBrick prefix and suffix and an illegal PstI restriction site near the HIS3 promoter of p413-GPD was removed. In the resultant plasmid, pSB413-GPD (5828 bp), the BioBrick prefix and suffix is situated between the strong constitutive yeast GPD promoter (TDH3) and CYC1 terminator allowing for facile cloning and expression of translational units in yeast. Standard VF2 and VR primer binding sites are included and M13 primer binding sites bracket the promoter and terminator. The plasmid has a ColE1 origin and ampicillin resistance for replication in E. coli. It also contains a yeast CEN/ARS and HIS3-selectable marker to provide high fidelity maintenance and low copy number in S. cerevisiae.
For p413 GPD the illegal site lies in the His promoter but did not have a restriction site around it.
Validation of Psb416 GPD
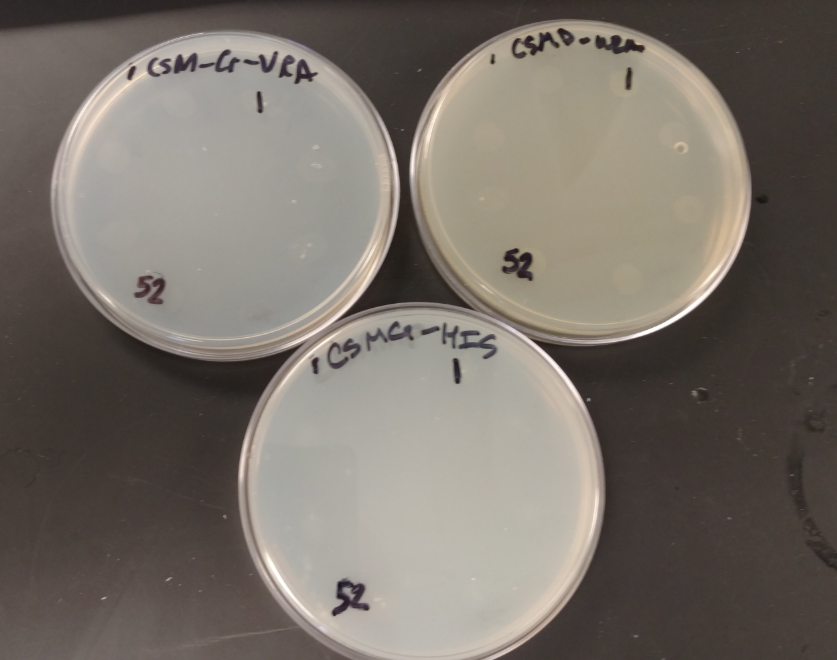
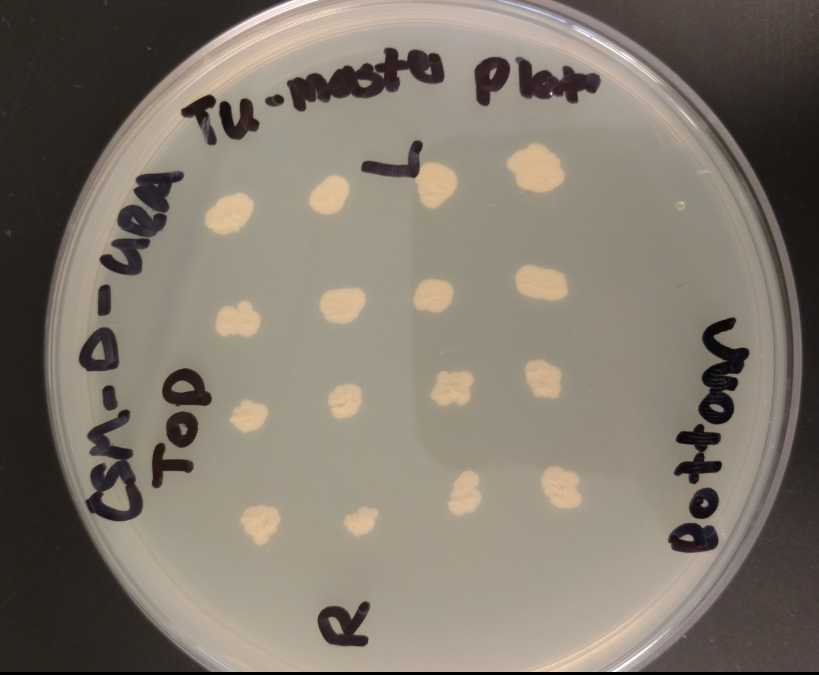
This process, however, does delete a few nucleotides from the Ura3 promoter region. To verify its function we transformed competent BY4741 Mat A, and BY4741 Mat A ynr036c yeast cells that have had their Ura3 genes knocked out.
BY4741 Mat A, and BY4741 Mat A ynr036c transformed with Psb416 GPD mRPS12 TU growing on CSM-Ura.
BY4741 Mat A, and BY4741 Mat A ynr036c without Psb416 GPD are unable to grow on CSM-Ura or CSM-His
As demonstrated above WT BY4741 yeast have their Ura3 gene knocked out and thus cannot grow on plates lacking uracil. Because BY4741 yeast that have been transformed with Psb416 GPD gain the ability to grow on CSM-Ura the alteration to the Ura3 promoter region must not have a significant impact on gene expression, allowing the transformants to produce their own Ura.
</span>