Aug.29th
pMV-G19 and pMV-G15 containing our target genes were received.
2.Colonies were used to inoculate overnight cultures.
Aug.30th
1.Plasmids were isolated using a miniprep kit.
2.Amplification of 19 and 15 with Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase out of E.coli.
19 amplification at 65.0°C with 19.rev/fwd primes.
PCR worked, positive control worked, no amplification of 19.
15 amplification at 65.0°C with 15.rev/fwd primes.
PCR worked, positive control worked, no amplification of 15.
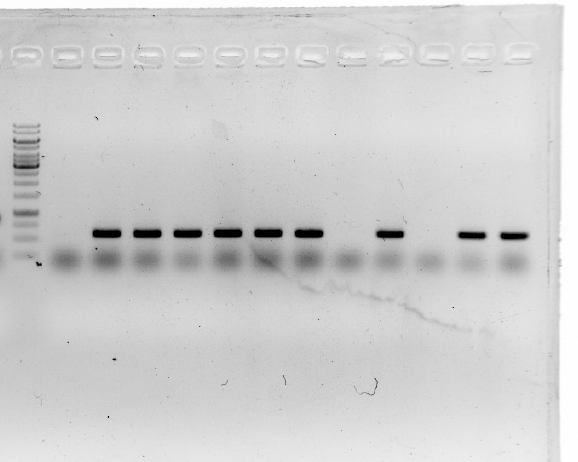
3.A product length of 900 bp was expected. The gel shows that most plasmids seem to be correct.
This result was confirmed by sequencing.
4.The fragments of 19 and 15 were purified with PCR Purification Kit.
Aug.31th
1.Ligation of 15 with 19.
2.We add a single 3`-adenine overhang to each end of the fragment of 19 and then purified with DNA Purification Kit.
3.19 was ligated into T vectors via TA clone and transformed into E.coli via heat shock.
Sep.1th
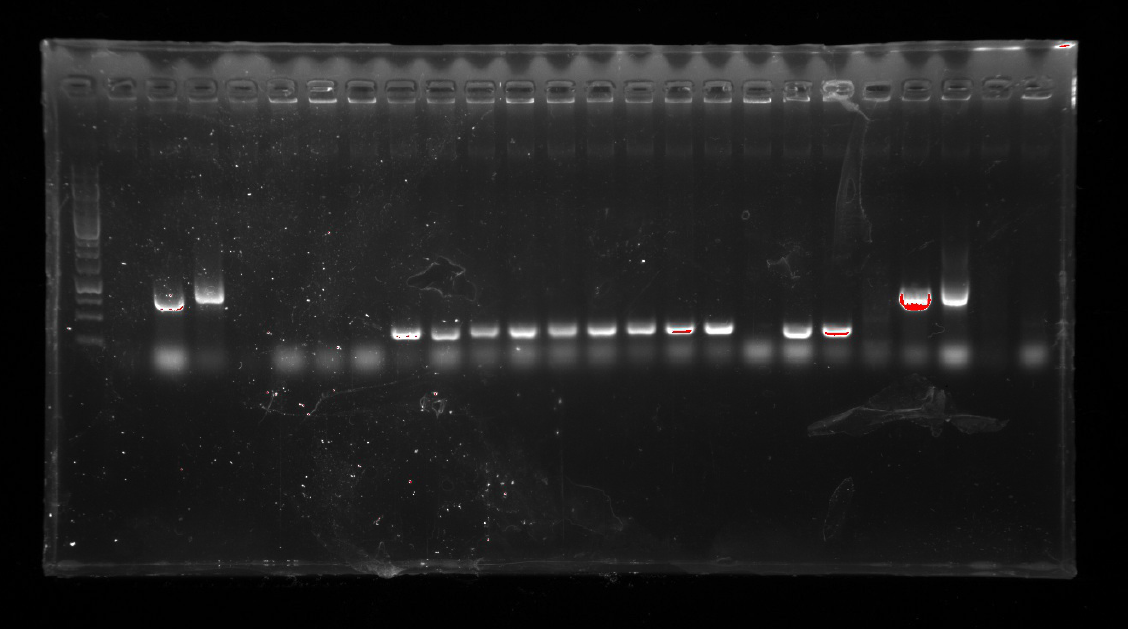
1.A colony PCR was performed with five colonies.
2.Gel electrophoresis showed that 5 colonies were positive for insertion of 19.
3.Two of these colonies containing 19 were used to inoculate overnight cultures.
4.15 gene fragment was phosphorylated.
Sep.2th
1.Plasmids containing T vector with
19(pT-19)were isolated using a miniprep kit.
2.Mono-restriction digest of pT-19 with stu I.
3.The enzyme-digested product was dephosphorylation.
4.Dephosphorylated plasmid and phosphorylated gene
15 were connected.
5.Ligation product was transformed into E.coli via heat shock.
Sep.3th
1.A colony PCR was performed with twelve colonies.
2.Gel electrophoresis showed that 2 colonies were positive for connecting the plasmid and gene fragment.
3.These two colonies were used to inoculate overnight cultures.