Design
BabbleBrick Format
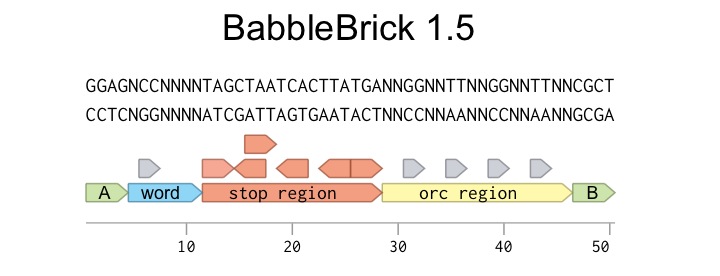
We went through an iterative design process with our BabbleBricks, which we have continued up to the Jamboree and will follow through on afterwards. Version 1.5 of the BabbleBrick is the standard we largely used in our proof of concept and summer work, and is the standard we submitted to the registry. Every BabbleBrick 1.5 has the format you can see here to the right.
A: The 5’ A type hang is produced upon digesting an AB type BabbleBrick with BsaI. It can anneal to the 3’ A hang of BA parts.
Word Coding Region: The coding signature that is unique in every BabbleBrick and is used to assign them meaning. Although it is referred to as a word coding region, it can be used to assign BabbleBricks other data values such as colours or numbers. There is a 2-nucleotide gap after the first nucleotide in the word coding region. This allows fine control of the BabbleBrick sequence to prevent restriction sites from appearing, making every possible nucleotide combination usable..
Stop Region: This 17 base pair long sequence introduces a stop codon into every reading frame within a BabbleBrick. This helps prevent large BabbleBrick constructs from producing any protein with their random sequences when replicating in cells. Read more about why we chose to include these here.
ORC Region: The ORC is a vector of error-correcting code intrinsic to each BabbleBrick. This helps rectify any errors introduced by mutation or poor-sequencing in the word coding region with high fidelity. Like the word coding region, it is staggered with nucleotides to allow fine control of the overall sequence. Read more about how an ORC works and our error-correcting functions here.
B: The 3’ ‘B’ type hang is produced upon digesting a BA type BabbleBrick with BsaI. It can anneal to the 5’ B hang of BA parts.




