(→Signal peptide collection) |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{LMU-TUM_Munich|navClass=part-collection}} | |
| − | {{LMU-TUM_Munich|navClass= | + | |
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | = | + | [[File:Muc16_BioBrick_summary_001.png |frameless|center|900px]] |
| + | |||
| + | =Signal peptide collection= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since signal peptides play an important role if you are woking on transmembrane constucts that are supposed to be secreted to the outer cell membrane we wanted to test some of the existing ones and submit new ones as well. | ||
| + | To achieve the best possible secretion of our eucaryotic receptors we tested three different signal peptides for their secretion efficiency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==BM40 signal peptide ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170214 BBa_K2170214])== | ||
| + | The BM40 signal peptide was designed by us, providing additional spacing as well as a Kozak sequence to the 5'-UTR of the constructs and combined with a BioBrick encoding the CMV promoter sequence ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K747096 BBa_K747096]) via the RFC10 cloning standard. The secretion efficiency was tested by NanoGlo Assay. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170214 BBa_K2170214] was used for all our eucaryotic receptor constructs ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170000 BBa_K2170000], [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170001 BBa_K2170001],[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170002 BBa_K2170002]). | ||
| − | == | + | ==Ig Kappa signal peptide ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170215 BBa_K2170215])== |
| − | + | The IgKappa signal peptide was designed by us, providing additional spacing as well as a Kozak sequence to the 5'-UTR of the constructs and combined with a BioBrick encoding the CMV promoter sequence ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K747096 BBa_K747096]) via the RFC10 cloning standard. The secretion efficiency was tested by NanoGlo Assay after the assembly of a testing device ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170012 BBa_K2170012]). | |
| − | == | + | =Eucaryotic receptor toolbox= |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | All eucaryotic [https://2016.igem.org/Team:LMU-TUM_Munich/Localization receptors] that we designed share a similar structure and were developed for use in eucaryotic cells. | |
| − | == | + | == Biotin presenting receptor with BAP ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170000 BBa_K2170000])== |
| − | + | ||
| − | Fusion protein with | + | Fusion protein with a Biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) for intracellular biotinylation by biotin ligase BirA. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane. The Biobrick contains an internal ribosomal binding site in front of the BirA so that it, although it is part of the same mRNA, is translated seperately from the rest of the transcript. The fusion protein is directed to the cellmembrane where it presents the biotinylated BAP on the surface where it can be bound by free streptavidin to impart a polymerization reaction between the cells which makes the scaffold free printing even possible. At the C terminal end of the BAP a Nanoluciferase was introduced so that the correct location of the receptor could be tested by NanoGlo-Assay. |
| − | == | + | ==Biotin binding receptor with eMa ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170001 BBa_K2170001])== |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | This BioBrick contains an eucaryotic receptor construct with enhanced monomeric avidin, which, after expression in an eucaryotic cell, imparts the binding of biotin on the cell surface. This constucts makes it possible to link cells over a biotinylated protein linker and by this makes the printing of tissue without scaffold even possible. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane. | |
| − | + | ==Biotin binding receptor with scAvidin ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170002 BBa_K2170002])== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | This BioBrick contains an eucaryotic receptor construct with single chain avidin, which, after expression in an eucaryotic cell, imparts the binding of biotin on the cell surface. This constucts makes it possible to link cells over a biotinylated protein linker and by this makes the printing of tissue without scaffold even possible. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane. | |
| − | == | + | =Procaryotic receptor collection= |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Biotin binding receptor with eMA ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170050 BBa_K2170050])== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | This BioBrick contains a biotin binding receptor with enhanced monomeric Avidin, which is presented on the cellsurface of procaryotic cell to bind biotin and with this, imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the eMA through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to bind biotinylated protein linkers. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct. The expression is controlled by a TetR-TetO system and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Biotin presenting receptor with BAP ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170051 BBa_K2170051])== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | This BioBrick contains a biotin presenting receptor with a biotin acceptor peptide, which is intracellularly biotinylated, and presented on the surface of the procaryotic cell so that the biotin can be bound by free strapavdin. This interaction imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the BAP through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to be bound. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct, as well as a NanoLuc, that enables the analysis of secretion efficiency by NanoGlo Assay. The expression is controlled by a TetR-TetO system and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline. | ||
| + | ==Biotin binding receptor with scAvidin ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170052 BBa_K2170052])== | ||
| − | + | This BioBrick contains a biotin binding receptor with single chain Avidin, which is presented on the cellsurface of procaryotic cell to bind biotin and with this, imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the scAvidin through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to bind biotinylated protein linkers. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct. The expression is controled by a TetR-TetO synstem and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | ||
<groupparts>iGEM2016 LMU-TUM_Munich</groupparts> | <groupparts>iGEM2016 LMU-TUM_Munich</groupparts> | ||
{{LMU-TUM_Munich_html_end}} | {{LMU-TUM_Munich_html_end}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:28, 20 October 2016
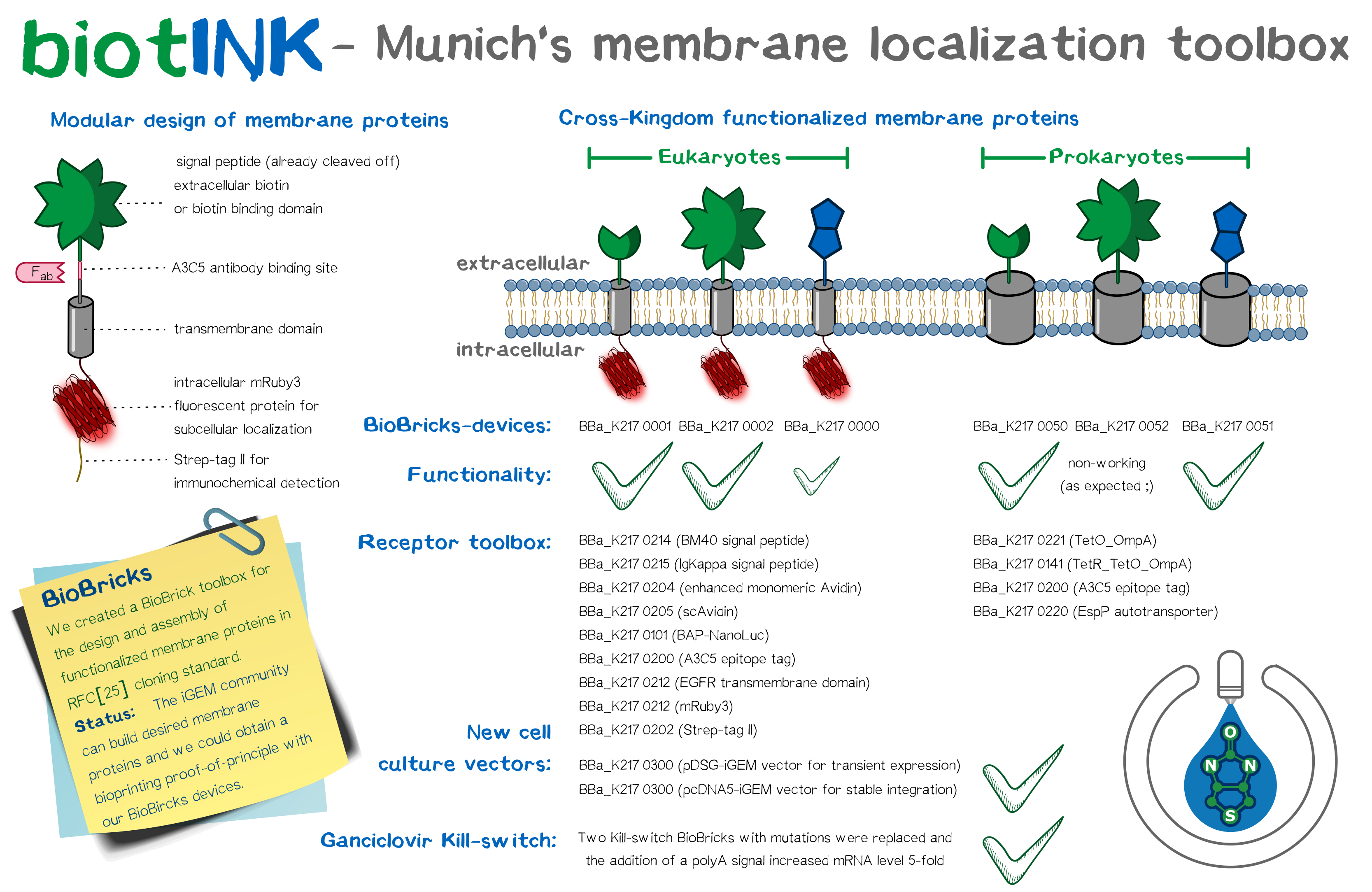
Signal peptide collection
Since signal peptides play an important role if you are woking on transmembrane constucts that are supposed to be secreted to the outer cell membrane we wanted to test some of the existing ones and submit new ones as well. To achieve the best possible secretion of our eucaryotic receptors we tested three different signal peptides for their secretion efficiency.
BM40 signal peptide ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170214 BBa_K2170214])
The BM40 signal peptide was designed by us, providing additional spacing as well as a Kozak sequence to the 5'-UTR of the constructs and combined with a BioBrick encoding the CMV promoter sequence ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K747096 BBa_K747096]) via the RFC10 cloning standard. The secretion efficiency was tested by NanoGlo Assay. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170214 BBa_K2170214] was used for all our eucaryotic receptor constructs ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170000 BBa_K2170000], [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170001 BBa_K2170001],[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170002 BBa_K2170002]).
Ig Kappa signal peptide ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170215 BBa_K2170215])
The IgKappa signal peptide was designed by us, providing additional spacing as well as a Kozak sequence to the 5'-UTR of the constructs and combined with a BioBrick encoding the CMV promoter sequence ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K747096 BBa_K747096]) via the RFC10 cloning standard. The secretion efficiency was tested by NanoGlo Assay after the assembly of a testing device ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170012 BBa_K2170012]).
Eucaryotic receptor toolbox
All eucaryotic receptors that we designed share a similar structure and were developed for use in eucaryotic cells.
Biotin presenting receptor with BAP ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170000 BBa_K2170000])
Fusion protein with a Biotin acceptor peptide (BAP) for intracellular biotinylation by biotin ligase BirA. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane. The Biobrick contains an internal ribosomal binding site in front of the BirA so that it, although it is part of the same mRNA, is translated seperately from the rest of the transcript. The fusion protein is directed to the cellmembrane where it presents the biotinylated BAP on the surface where it can be bound by free streptavidin to impart a polymerization reaction between the cells which makes the scaffold free printing even possible. At the C terminal end of the BAP a Nanoluciferase was introduced so that the correct location of the receptor could be tested by NanoGlo-Assay.
Biotin binding receptor with eMa ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170001 BBa_K2170001])
This BioBrick contains an eucaryotic receptor construct with enhanced monomeric avidin, which, after expression in an eucaryotic cell, imparts the binding of biotin on the cell surface. This constucts makes it possible to link cells over a biotinylated protein linker and by this makes the printing of tissue without scaffold even possible. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane.
Biotin binding receptor with scAvidin ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170002 BBa_K2170002])
This BioBrick contains an eucaryotic receptor construct with single chain avidin, which, after expression in an eucaryotic cell, imparts the binding of biotin on the cell surface. This constucts makes it possible to link cells over a biotinylated protein linker and by this makes the printing of tissue without scaffold even possible. It's expression is regulated by a CMV promotor and its secretion guided by a BM40 signal peptide. For better characterization a mRuby3 was added to the intracellular part of the fusion protein. Also an A3C5-Tag (intracellular), an antibody binding site, as well as a Strep TagII, a binding sequence for streptavidin, was added to have different possibilities for later characterization of the transfected construct. The intr- and extracellular parts are connected by an EGFR TMD with stop transfer signal, which makes sure that the TMD stays inside the membrane.
Procaryotic receptor collection
Biotin binding receptor with eMA ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170050 BBa_K2170050])
This BioBrick contains a biotin binding receptor with enhanced monomeric Avidin, which is presented on the cellsurface of procaryotic cell to bind biotin and with this, imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the eMA through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to bind biotinylated protein linkers. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct. The expression is controlled by a TetR-TetO system and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline.
Biotin presenting receptor with BAP ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170051 BBa_K2170051])
This BioBrick contains a biotin presenting receptor with a biotin acceptor peptide, which is intracellularly biotinylated, and presented on the surface of the procaryotic cell so that the biotin can be bound by free strapavdin. This interaction imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the BAP through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to be bound. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct, as well as a NanoLuc, that enables the analysis of secretion efficiency by NanoGlo Assay. The expression is controlled by a TetR-TetO system and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline.
Biotin binding receptor with scAvidin ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2170052 BBa_K2170052])
This BioBrick contains a biotin binding receptor with single chain Avidin, which is presented on the cellsurface of procaryotic cell to bind biotin and with this, imparts the polymerization of our cells. Because of the OmpA the receptor is secreted via the SEC pathway into the outer membrane. The EspP-Autotransporter, which is on the C-terminal side of the fusion protein, pushes the scAvidin through the outer membrane and presents it on the cell surface where it is ready to bind biotinylated protein linkers. For localisation analysis an A3C5 Tag was added to the construct. The expression is controled by a TetR-TetO synstem and can be induced by addition of Tetracycline.
<groupparts>iGEM2016 LMU-TUM_Munich</groupparts>